Last updated on December 18th, 2024 at 03:24 am
- 1. Understanding Antidepressants and Their Effects
- 1.1 Types of Antidepressants
- 1.2 Therapeutic Uses
- 2. The Phenomenon of Antidepressant Withdrawal
- 2.1 Factors Influencing Withdrawal Severity
- 2.2 Common Withdrawal Symptoms
- 3. The Controversy: Withdrawal vs. Discontinuation Syndrome
- 3.1 The Case for “Discontinuation Syndrome”
- 3.2 Arguments for “Withdrawal”
- 4. The Neurobiology of Antidepressant Withdrawal
- 4.1 Neurotransmitter Imbalance
- 4.2 Receptor Adaptation
- 5. Distinguishing Withdrawal from Relapse
- 5.1 Characteristics of Withdrawal
- 5.2 Signs of Depressive Relapse
- 6. The Importance of Gradual Tapering
- 6.1 Tapering Strategies
- 6.2 Challenges in Tapering
- 7. Managing Withdrawal Symptoms
- 7.1 Supportive Care
- 7.2 Symptomatic Treatment
- 8. The Role of Psychotherapy in Antidepressant Discontinuation
- 8.1 Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- 8.2 Mindfulness-Based Approaches
- 9. Long-Term Considerations
- 9.1 Relapse Prevention
- 9.2 Alternative Treatment Modalities
- 10. Future Directions in Antidepressant Research and Management
- 10.1 Novel Antidepressant Formulations
- 10.2 Personalized Medicine Approaches
- Addressing Psychological Symptoms During Antidepressant Withdrawal
- Navigating the Discontinuation Symptoms and Intense Withdrawal
- The Role of Medical Detox Programs
- Holistic Approaches to Antidepressant Detoxification
- Psychological and Emotional Symptoms of Withdrawal
- Addressing Physical Symptoms and Withdrawal Effects
- Relapse Prevention Strategies Post-Withdrawal
- The Difference Between Withdrawal Symptoms and Relapse of Depression
- Managing Intense Symptoms With Proper Support
- Incorporating Lifestyle Changes and Natural Remedies for Antidepressant Withdrawal
- Treatment Plans for Antidepressant Dependence and Withdrawal Management
- Comprehensive Care for Ongoing Symptoms
- Addressing the Risk of Withdrawal Syndrome Through Tapering Strategies
- Navigating Abrupt Discontinuation and the Risks Involved
- Antidepressant Withdrawal and Mental Health Conditions
- Addiction Counseling as Part of the Recovery Process
- Coping With Antidepressant Withdrawal Symptoms in Daily Life
- Understanding Physical Dependence and the Withdrawal Process
- Complementary Therapies for Withdrawal Management
- Differentiating Between Common Symptoms and Severe Symptoms
- Ongoing Treatment and Recovery Journey
- Antidepressant Discontinuation Syndrome: A Closer Look
- Emotional Symptoms and Antidepressant Withdrawal Effects on the Brain
- Exploring Tapering Assistance Programs for Safe Withdrawal
- Medical Care During Antidepressant Withdrawal
- Addressing Withdrawal Side Effects in the Recovery Process
- The Impact of Antidepressant Withdrawal on Physical Health
- Antidepressant Withdrawal and the Role of Healthcare Professionals
- Coping Strategies for Antidepressant Withdrawal Anxiety
- Antidepressant Withdrawal and Its Long-Term Effects
- Importance of Health Insurance in the Withdrawal Process
- Differences in Brain Chemistry During Withdrawal
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What Are The Common Symptoms Of Antidepressant Discontinuation Syndrome?
- How Can Tapering Off Antidepressants Safely Be Achieved?
- What Are The Psychological Symptoms Of Antidepressant Withdrawal?
- Are Brain Zaps A Common Symptom During Antidepressant Withdrawal?
- How Long Does Antidepressant Withdrawal Usually Last?
- What Is The Difference Between Withdrawal Symptoms And A Relapse Of Depression?
- Can Abrupt Discontinuation Of Antidepressants Be Dangerous?
- How Can Antidepressant Discontinuation Syndrome Be Managed?
- What Are The Potential Risks Of Not Seeking Professional Guidance During Antidepressant Withdrawal?
- How Can Healthcare Professionals Assist With Antidepressant Detoxification?
- What Holistic Approaches Are Available For Antidepressant Withdrawal?
- How Does Antidepressant Withdrawal Affect Brain Chemistry?
- Are There Differences In Withdrawal Symptoms Between Short And Long-Acting Antidepressants?
- What Role Does Medical Detox Play In Antidepressant Withdrawal?
- Can Antidepressant Withdrawal Cause Physical Symptoms?
- What Are Effective Treatment Options For Antidepressant Discontinuation Syndrome?
- How Can Emotional Symptoms During Antidepressant Withdrawal Be Managed?
- Is Antidepressant Detoxification A Part Of Recovery From Clinical Depression?
- How Can Withdrawal Symptoms Be Alleviated Naturally During Antidepressant Discontinuation?
- How Does Antidepressant Withdrawal Impact Daily Life?
Antidepressant medications have become increasingly prevalent in modern society, offering relief to millions suffering from depression and related mental health conditions. However, the process of discontinuing these medications can present significant challenges.
This comprehensive exploration delves into the intricacies of antidepressant withdrawal, detoxification, and the broader implications for individuals seeking to transition away from these powerful psychoactive substances.
Let’s discover how to safely manage antidepressant withdrawal and detox with expert guidance, effective strategies, and personalized support for a smoother recovery journey.
1. Understanding Antidepressants and Their Effects
Antidepressants encompass a diverse group of medications designed to alleviate symptoms associated with depression and other mental health disorders. These drugs typically work by modulating neurotransmitter levels in the brain, particularly serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine.
1.1 Types of Antidepressants
There are several classes of antidepressants, each with unique mechanisms of action:
– Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
– Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
– Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
– Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
– Atypical Antidepressants
1.2 Therapeutic Uses
While primarily prescribed for depression, antidepressants have found efficacy in treating various conditions:
– Anxiety disorders
– Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
– Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
– Chronic pain syndromes
– Eating disorders
2. The Phenomenon of Antidepressant Withdrawal
Discontinuing antidepressant medication can trigger a range of symptoms collectively known as antidepressant withdrawal or discontinuation syndrome. This phenomenon occurs due to the brain’s sudden adjustment to the absence of the medication.
2.1 Factors Influencing Withdrawal Severity
Several factors can impact the intensity and duration of withdrawal symptoms:
– Duration of antidepressant use
– Dosage
– Type of antidepressant
– Individual physiology
– Method of discontinuation (abrupt vs. gradual)
2.2 Common Withdrawal Symptoms
Antidepressant withdrawal can manifest through various physical and psychological symptoms:
– Flu-like symptoms (nausea, headache, fatigue)
– Sensory disturbances (dizziness, vertigo)
– Gastrointestinal issues
– Sleep disturbances
– Mood changes (irritability, anxiety)
– Cognitive effects (confusion, difficulty concentrating)

3. The Controversy: Withdrawal vs. Discontinuation Syndrome
The terminology used to describe the effects of stopping antidepressants has been a subject of debate within the medical community. While some professionals prefer the term “discontinuation syndrome,” others argue that “withdrawal” more accurately reflects the experience.
3.1 The Case for “Discontinuation Syndrome”
Proponents of this term argue that it distinguishes the process from drug addiction withdrawal, emphasizing that antidepressants are not considered addictive in the traditional sense.
3.2 Arguments for “Withdrawal”
Those advocating for the use of “withdrawal” contend that it more accurately conveys the potential severity and impact of stopping antidepressants, preventing the minimization of patients’ experiences.
4. The Neurobiology of Antidepressant Withdrawal
Understanding the neurobiological mechanisms underlying antidepressant withdrawal provides insight into why these symptoms occur and how they can be managed.
4.1 Neurotransmitter Imbalance
Antidepressants alter the brain’s neurotransmitter systems over time. Abrupt discontinuation can lead to a sudden imbalance, triggering withdrawal symptoms.
4.2 Receptor Adaptation
Long-term antidepressant use can cause changes in neurotransmitter receptor sensitivity. When the medication is stopped, these adaptations can result in temporary dysfunction.


5. Distinguishing Withdrawal from Relapse
One of the challenges in managing antidepressant discontinuation is differentiating between withdrawal symptoms and a recurrence of the original depressive condition.
5.1 Characteristics of Withdrawal
– Typically begins within days of stopping or reducing medication
– Symptoms often include physical complaints not present in the original depression
– Tends to be time-limited, resolving within weeks
5.2 Signs of Depressive Relapse
– May occur weeks or months after discontinuation
– Symptoms closely mirror the original depressive episode
– Often more persistent and may worsen over time
6. The Importance of Gradual Tapering
Abruptly stopping antidepressant medication can lead to severe withdrawal symptoms and increase the risk of relapse. Gradual tapering is crucial for minimizing these risks.
6.1 Tapering Strategies
– Slow reduction of dosage over weeks or months
– Individualized approach based on medication type and patient factors
– Close monitoring and adjustment of the tapering schedule as needed
6.2 Challenges in Tapering
– Limited availability of appropriate dosage forms
– Individual variability in response to dose reductions
– Psychological dependence and fear of discontinuation


7. Managing Withdrawal Symptoms
While tapering can significantly reduce the severity of withdrawal, some individuals may still experience symptoms. Various strategies can help manage these effects.
7.1 Supportive Care
– Adequate rest and sleep hygiene
– Balanced nutrition and hydration
– Gentle exercise and stress-reduction techniques
7.2 Symptomatic Treatment
– Short-term use of medications to address specific symptoms (e.g., anti-nausea drugs, sleep aids)
– Non-pharmacological interventions such as acupuncture or cognitive-behavioral therapy
8. The Role of Psychotherapy in Antidepressant Discontinuation
Psychotherapy can play a crucial role in supporting individuals through the process of discontinuing antidepressants and beyond.
8.1 Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT can help individuals develop coping strategies for managing withdrawal symptoms and addressing underlying psychological issues.
8.2 Mindfulness-Based Approaches
Mindfulness techniques can assist in managing anxiety and mood fluctuations associated with antidepressant withdrawal.
9. Long-Term Considerations
The decision to discontinue antidepressants should be made with careful consideration of long-term implications and strategies for maintaining mental health.
9.1 Relapse Prevention
– Developing a robust support system
– Identifying and addressing potential triggers
– Regular follow-up with mental health professionals
9.2 Alternative Treatment Modalities
– Exploring non-pharmacological approaches to managing depression and anxiety
– Lifestyle modifications to support mental health (e.g., diet, exercise, sleep hygiene)


10. Future Directions in Antidepressant Research and Management
As our understanding of depression and antidepressant mechanisms evolves, new approaches to treatment and discontinuation are emerging.
10.1 Novel Antidepressant Formulations
Research into new antidepressant medications with reduced withdrawal potential and improved efficacy continues.
10.2 Personalized Medicine Approaches
Advances in genetic testing and biomarker identification may lead to more tailored antidepressant prescribing and discontinuation strategies.
Addressing Psychological Symptoms During Antidepressant Withdrawal
Psychological symptoms such as anxiety, irritability, and vivid dreams are common during the antidepressant withdrawal process. Managing these symptoms often requires a comprehensive approach, including both medical and psychological support to ensure a safe and effective transition.
Regular sessions with a healthcare professional can help in monitoring these psychological symptoms. Additional support from mental health counselors ensures that patients have the right tools to cope effectively.
Navigating the Discontinuation Symptoms and Intense Withdrawal
Discontinuation symptoms can vary significantly depending on factors such as the current dose, type of antidepressant drugs, and the length of time it has been used. Individuals may experience initial withdrawal symptoms like brain zaps or electric shock sensations that can lead to intense withdrawal symptoms if not properly managed.
Consulting a healthcare provider can help establish a safer withdrawal strategy. Gradual tapering of antidepressants is often recommended to avoid the onset of severe symptoms during withdrawal.
The Role of Medical Detox Programs
Medical detox programs provide essential support for individuals experiencing severe withdrawal symptoms. Abrupt cessation of antidepressants can increase the risk of severe withdrawal symptoms, which is why supervised medical detox can help minimize both physical symptoms and mental health conditions associated with discontinuation.
An inpatient detox program offers a structured approach to managing severe symptoms and ensures comprehensive care during the withdrawal period. Medical professionals can adjust the detox process according to the patient’s medical history and ongoing symptoms.
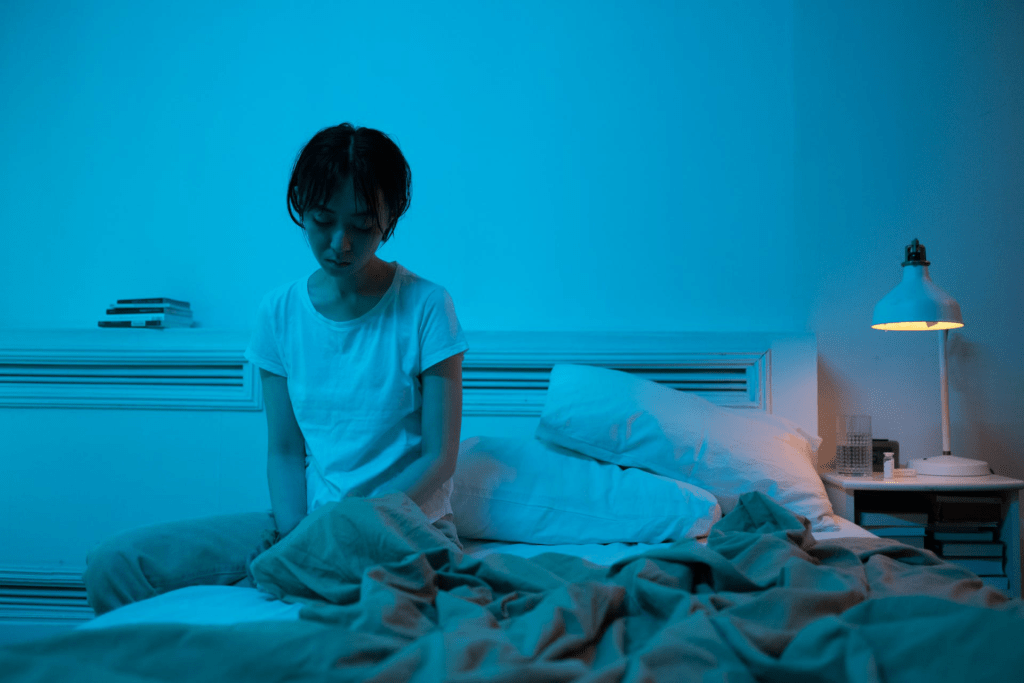


Holistic Approaches to Antidepressant Detoxification
Holistic therapies, such as acupuncture and mindfulness-based cognitive therapy, can help alleviate uncomfortable withdrawal symptoms. These therapies offer support beyond medications, helping to restore emotional balance and minimize physical dependence.
Incorporating holistic approaches, like yoga exercises and meditation practices, can effectively aid in managing withdrawal symptoms and reducing the severity of withdrawal symptoms. These activities are beneficial for reducing stress and enhancing overall physical health.
Psychological and Emotional Symptoms of Withdrawal
Emotional symptoms such as mood swings, depressive symptoms, and crying spells can surface during antidepressant withdrawal. It is important to differentiate these from a relapse of depression.
Ongoing treatment, including regular sessions with a mental health counselor, can provide emotional and psychological support. Family therapy sessions may also assist in easing these emotional symptoms and support individuals’ daily lives during the recovery journey.
Addressing Physical Symptoms and Withdrawal Effects
Common symptoms such as gastrointestinal issues, headaches, and loss of coordination are examples of physical symptoms individuals may encounter during antidepressant withdrawal. Complementary therapies, including herbal supplements like omega-3 and vitamin B complex, are often recommended to mitigate these physical health concerns.
Maintaining a balanced antidepressant withdrawal diet plan and staying hydrated can further alleviate physical symptoms. A focus on physical health ensures that patients are more resilient to ongoing symptoms.
Relapse Prevention Strategies Post-Withdrawal
Once the withdrawal process is complete, relapse prevention remains a critical component of recovery. The risk of withdrawal and relapse of depression can be mitigated by maintaining a comprehensive care plan, which may include ongoing therapy, support groups, and lifestyle modifications.
Engaging with antidepressant withdrawal support groups, either in-person or online, can offer valuable peer support during this phase of the recovery process. Staying connected with supportive communities helps build resilience against depressive symptoms.
The Difference Between Withdrawal Symptoms and Relapse of Depression
Identifying the difference between withdrawal symptoms and a relapse of depression is crucial for proper care. Withdrawal symptoms are typically time-limited and can present through clusters of symptoms like electric shock sensations, vivid dreams, and mood swings.
In contrast, a relapse may present as a re-emergence of symptoms of depression that persists for an extended period. Consulting healthcare professionals can help in distinguishing these conditions and managing them appropriately.
Managing Intense Symptoms With Proper Support
For individuals experiencing extreme withdrawal symptoms, such as panic attacks or suicidal ideation, immediate intervention from a medical professional is essential. Medical detox or addiction counseling can be beneficial in cases involving severe symptoms.
Moreover, healthcare professionals may provide medications for symptom management to ease severe withdrawal symptoms during critical moments of withdrawal. Proper care can significantly reduce the severity of intense symptoms.


Incorporating Lifestyle Changes and Natural Remedies for Antidepressant Withdrawal
Making lifestyle changes can aid significantly in managing the severity of withdrawal symptoms. Introducing regular exercise, such as yoga and meditation, can promote better emotional regulation and reduce anxiety.
Natural remedies for antidepressant withdrawal, including mindfulness techniques and herbal supplements, may also help alleviate uncomfortable withdrawal symptoms and support individuals on their path to recovery. For more information, Harvard Health Publishing provides additional insights into these approaches.
Treatment Plans for Antidepressant Dependence and Withdrawal Management
Creating individualized treatment plans is essential for managing antidepressant dependence and withdrawal. These treatment options often include tapering off antidepressants safely under medical supervision, alongside therapies like addiction counseling.
Healthcare providers may also consider longer-acting antidepressant medications to facilitate a smoother withdrawal process. More detailed guidance can be found on Enlightened Recovery Solutions.
Comprehensive Care for Ongoing Symptoms
Ongoing symptoms, such as insomnia or mood regulation challenges, require a multifaceted approach involving both pharmacological and non-pharmacological methods. Medical detoxification programs often work in conjunction with therapies to provide effective management.
For more resources, Harvard Medical School and Immersion Recovery Center offer detailed information on managing ongoing symptoms post-withdrawal. These centers can provide clinical support to ease the recovery process.
Addressing the Risk of Withdrawal Syndrome Through Tapering Strategies
Tapering off antidepressants safely is key to minimizing the risk of antidepressant withdrawal syndrome. The dosage over time can be gradually decreased to reduce the intensity of withdrawal symptoms, often over successive intervals determined by the healthcare provider.
A detailed guide for tapering strategies can be found on Reuptake Inhibitor Guide, providing a structured plan for those aiming to discontinue antidepressant medications. Individualized tapering schedules can make the withdrawal process more manageable.
Navigating Abrupt Discontinuation and the Risks Involved
Abrupt discontinuation of antidepressants can significantly increase the risk of severe withdrawal symptoms. Such symptoms may include electric shock-like sensations, vivid dreams, and severe mood swings.
It is advisable to work with healthcare professionals to avoid the uncomfortable withdrawal symptoms that often accompany abrupt cessation. Gradual reduction in dosage helps to prevent extreme withdrawal symptoms.


Antidepressant Withdrawal and Mental Health Conditions
Antidepressant withdrawal is often compounded by co-occurring mental health conditions, such as generalized anxiety disorder or major depression. Addressing these conditions with a medical professional is crucial to ensure that the withdrawal process does not exacerbate underlying issues.
Effective management strategies are necessary to avoid the relapse of depression and other mood disorders. Proper treatment can enhance overall emotional balance and stability during withdrawal.
Addiction Counseling as Part of the Recovery Process
Addiction counseling, including both one-to-one therapy and family therapy sessions, can be beneficial in navigating the withdrawal process. These approaches help manage psychiatric symptoms like intense mood swings, panic attacks, and emotional numbness.
Addiction counseling also provides support for those with a history of psychosis or substance use disorders. Integrating these sessions into the treatment plan can reduce the risk of relapse and promote emotional well-being.
Coping With Antidepressant Withdrawal Symptoms in Daily Life
Managing antidepressant withdrawal symptoms, such as fatigue, gastrointestinal issues, and vivid dreams, is essential for maintaining normal daily life. Engaging in lifestyle changes like exercise and maintaining good sleep hygiene can help alleviate these symptoms.
Proper care from healthcare providers, along with complementary therapies, can make a significant difference in the recovery journey. It ensures patients regain stability in their everyday tasks.
Understanding Physical Dependence and the Withdrawal Process
Antidepressant withdrawal often involves both psychological and physical symptoms, resulting from physical dependence on the medication. Symptoms like electric shock sensations, headaches, and gastrointestinal disturbances are common.
A gradual reduction of the prescribed dose over an extended period can help minimize these physical symptoms and mitigate severe withdrawal effects. Proper management of physical symptoms is critical for effective withdrawal.
Complementary Therapies for Withdrawal Management
Complementary therapies such as acupuncture, herbal supplements, and mindfulness-based techniques can provide substantial support for individuals experiencing antidepressant withdrawal. These therapies are particularly helpful in managing physical and behavioral symptoms that may persist throughout the withdrawal period.
Regular sessions with a mental health counselor can further enhance the effectiveness of these therapies. Integrating both conventional and holistic methods can lead to better withdrawal outcomes.


Differentiating Between Common Symptoms and Severe Symptoms
Withdrawal can present with a range of symptoms, from mild symptoms like dizziness and nausea to severe symptoms such as intense withdrawal symptoms and panic attacks. Understanding the severity of withdrawal symptoms and recognizing early warning signs can help healthcare providers adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Gradual tapering and medical detox programs are often the preferred options to manage these diverse symptoms. Proper symptom classification ensures that patients receive appropriate care.
Ongoing Treatment and Recovery Journey
The recovery journey from antidepressant withdrawal is often long and requires continued support. Ongoing symptoms like muscle aches, restlessness, and mood swings can persist for an extended period.
Effective treatment plans, including both medical and holistic interventions, can support individuals as they navigate these challenges, ultimately aiding in a successful path to recovery. Continued care is vital for sustained recovery.
Antidepressant Discontinuation Syndrome: A Closer Look
Antidepressant discontinuation syndrome is a term often used to describe the collection of symptoms that occur after stopping antidepressant medication. This syndrome includes symptoms such as flu-like symptoms, electric shock sensations, and emotional symptoms like crying spells.
Healthcare professionals may recommend medications for symptom management to alleviate these ongoing symptoms during the discontinuation period. Proper intervention is essential to ease these effects and improve overall well-being.
Emotional Symptoms and Antidepressant Withdrawal Effects on the Brain
Emotional symptoms such as mood swings, irritability, and crying spells are a result of changes in brain chemistry during withdrawal. These symptoms are linked to altered serotonin levels and receptor adaptation, which occur as the body adjusts to the absence of antidepressant drugs.
A combination of psychotherapy and medical supervision can help manage these emotional fluctuations. Emotional support is a vital component of the overall withdrawal treatment plan.
Exploring Tapering Assistance Programs for Safe Withdrawal
Tapering assistance programs, involving healthcare professionals, are designed to help individuals safely reduce their antidepressant dosage over time. These programs often incorporate psychological support, medications for symptom management, and peer counseling.
Resources like Clock Medical provide guidance on the best tapering protocols for individual needs. Structured assistance can make the tapering process smoother and more successful.
Medical Care During Antidepressant Withdrawal
Proper medical care is essential for individuals discontinuing antidepressant treatment. This includes monitoring by healthcare professionals to manage withdrawal syndrome and prevent the relapse of depressive disorder.
Clinical care, including both inpatient and outpatient services, can provide the necessary support for managing potential symptoms throughout the withdrawal process. A consistent medical approach helps mitigate risks during withdrawal.


Addressing Withdrawal Side Effects in the Recovery Process
Side effects such as nausea, dizziness, and concentration problems are common during withdrawal. These side effects can disrupt daily life and interfere with everyday tasks.
Medical professionals can assist in addressing these symptoms through medications for symptom management, as well as non-pharmacological interventions like acupuncture or natural remedies. Proper intervention ensures a smoother recovery journey.
The Impact of Antidepressant Withdrawal on Physical Health
Antidepressant withdrawal can have significant effects on physical health, including issues with balance, gastrointestinal disturbances, and headaches. Maintaining proper hydration and a balanced diet can help minimize these physical symptoms.
In addition, vitamin B complex and omega-3 supplements may offer added support during the withdrawal process. Supporting physical health plays a crucial role in ensuring a successful withdrawal.
Antidepressant Withdrawal and the Role of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in the withdrawal process. Their involvement is critical for tapering strategies, monitoring ongoing symptoms, and adjusting treatment plans as needed.
Collaborative care between medical professionals and mental health counselors ensures that individuals receive comprehensive support during this challenging period. Proper healthcare supervision minimizes withdrawal complications.
Coping Strategies for Antidepressant Withdrawal Anxiety
Antidepressant withdrawal anxiety can be managed through a combination of medications, therapy, and holistic methods. Techniques like mindfulness meditation, acupuncture, and cognitive-behavioral therapy have shown effectiveness in alleviating anxiety symptoms.
Access to mental health hotlines and peer support groups can also provide immediate relief during particularly challenging moments. Continuous support reduces the likelihood of withdrawal anxiety.
Antidepressant Withdrawal and Its Long-Term Effects
Antidepressant withdrawal can have long-term effects on emotional balance and physical health. Some individuals may experience lingering symptoms such as fatigue, emotional numbness, and sensory disturbances.
Long-term support, such as psychiatric medication for symptom management and ongoing therapy, can help individuals regain stability and improve their quality of life. Sustained care is essential for achieving lasting emotional and physical recovery.
Importance of Health Insurance in the Withdrawal Process
Health insurance can be instrumental in covering the costs associated with antidepressant withdrawal treatment options. Coverage may include medical detox programs, addiction counseling, and therapy sessions.
It is advisable to consult with insurance providers to understand the level of care available during the withdrawal process, ensuring access to the necessary treatment options for effective management. Proper insurance coverage eases the financial burden of withdrawal.
Differences in Brain Chemistry During Withdrawal
The withdrawal period is marked by significant changes in brain chemistry, including fluctuations in serotonin levels. This can lead to uncomfortable symptoms such as brain zaps, vivid dreams, and emotional instability.
Addressing these differences in brain chemistry is essential for managing antidepressant withdrawal and ensuring a smoother recovery journey. Proper management of brain chemistry helps maintain emotional stability during withdrawal.


Conclusion
The process of discontinuing antidepressant medication is complex and multifaceted, requiring careful consideration, professional guidance, and individualized approaches. By understanding the mechanisms of withdrawal, implementing appropriate tapering strategies, and utilizing supportive interventions, individuals can navigate this challenging transition more effectively.
As research in this field progresses, it is hoped that improved methods for managing antidepressant discontinuation will emerge, ultimately leading to better outcomes for those seeking to move beyond antidepressant therapy.
From Embrace Inner Chaos to your inbox
Transform your Chaos into authentic personal growth – sign up for our free weekly newsletter! Stay informed on the latest research advancements covering:
Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD)
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Common Symptoms Of Antidepressant Discontinuation Syndrome?
Antidepressant discontinuation syndrome is characterized by a variety of symptoms that can affect both mental and physical health. These symptoms often include vivid dreams, mood swings, electric shock sensations, and brain zaps.
The onset of these symptoms typically occurs when someone abruptly discontinues or reduces their current dose of antidepressants. The intensity of withdrawal symptoms depends on the type of antidepressant and the duration of use. The Mayo Clinic emphasizes that medical supervision is crucial to avoid severe withdrawal symptoms during the discontinuation process.
How Can Tapering Off Antidepressants Safely Be Achieved?
Tapering off antidepressants safely requires a well-structured plan created with a healthcare provider to minimize withdrawal symptoms. Gradual dose reduction over an extended period is commonly recommended to allow the body to adjust slowly to the decreasing levels of serotonin.
Healthcare professionals, such as mental health counselors, stress the importance of personalized tapering schedules to reduce the risk of abrupt cessation effects, such as intense withdrawal symptoms or even a relapse of depression. According to WebMD, understanding individual medical history is critical for effectively tapering antidepressants.
What Are The Psychological Symptoms Of Antidepressant Withdrawal?
Psychological symptoms of antidepressant withdrawal can manifest in various forms, such as intense mood swings, suicidal ideation, and severe symptoms of anxiety. These symptoms are particularly distressing and can often interfere with daily life.
A person experiencing psychological withdrawal symptoms might also feel a return of depressive symptoms or develop new conditions like panic attacks. Healthline advises working with a medical professional to address these symptoms, as they are often indicative of the body struggling to regain balance.
Are Brain Zaps A Common Symptom During Antidepressant Withdrawal?
Brain zaps, often described as electric shock-like sensations in the brain, are a common experience during antidepressant withdrawal. These shocks may occur randomly and are linked to changes in serotonin levels in the brain due to the discontinuation of antidepressants.
Brain zaps can be alarming but are generally harmless and tend to diminish over time. According to Harvard Health Publishing, gradual tapering of medication is recommended to reduce the frequency of brain zaps and similar symptoms.
How Long Does Antidepressant Withdrawal Usually Last?
The duration of antidepressant withdrawal varies significantly depending on the individual’s previous dose, duration of medication use, and type of antidepressant. Symptoms may begin within a few days of stopping the medication and can last anywhere from a few weeks to several months.
The withdrawal period can be shorter for longer-acting antidepressants compared to those with a shorter half-life. Johns Hopkins Medicine suggests that individuals undergoing withdrawal be closely monitored by healthcare providers to prevent a relapse or prolonged symptoms.
What Is The Difference Between Withdrawal Symptoms And A Relapse Of Depression?
Withdrawal symptoms and relapse of depression can sometimes present similarly, making it difficult to distinguish between the two. Withdrawal symptoms often involve physical sensations, such as brain zaps, dizziness, and gastrointestinal issues.
A relapse of depression is more centered around the recurrence of depressive symptoms like prolonged sadness and hopelessness. The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) advises that differentiating between these conditions is essential, as treatment options and approaches can differ significantly.


Can Abrupt Discontinuation Of Antidepressants Be Dangerous?
Abrupt discontinuation of antidepressants can be dangerous, leading to severe withdrawal symptoms, including intense anxiety, agitation, electric shocks, and suicidal ideation. Stopping medication without a proper plan can also cause antidepressant discontinuation syndrome, which has a range of physical and psychological symptoms.
Cleveland Clinic recommends that anyone looking to stop antidepressants consult their healthcare provider to create a safe and effective tapering plan. This helps prevent complications and ensures a smoother withdrawal process.
How Can Antidepressant Discontinuation Syndrome Be Managed?
Managing antidepressant discontinuation syndrome requires a comprehensive approach, including proper tapering of medication, lifestyle modifications, and complementary therapies such as mindfulness and yoga. Medical professionals often suggest that individuals engage in behavioral therapies or join support groups to cope with uncomfortable withdrawal symptoms.
National Health Service (NHS) stresses the role of ongoing support and regular medical consultations in effectively managing withdrawal. Proper supervision ensures that symptoms are kept under control.
What Are The Potential Risks Of Not Seeking Professional Guidance During Antidepressant Withdrawal?
The risks of not seeking professional guidance during antidepressant withdrawal include a heightened chance of severe symptoms, such as suicidal ideation, physical dependence, and relapse into severe depression. Without proper guidance, individuals are at risk of severe withdrawal symptoms that could significantly impair their quality of life and interfere with everyday tasks.
American Psychological Association (APA) advises individuals to seek help from a mental health counselor or healthcare provider to ensure the withdrawal process is handled safely and effectively. Professional guidance can help alleviate much of the distress associated with withdrawal.
How Can Healthcare Professionals Assist With Antidepressant Detoxification?
Healthcare professionals play a vital role in the antidepressant detoxification process, which involves gradually reducing the medication dose under medical supervision to minimize withdrawal effects. They can also provide medications for symptom management and behavioral support to help patients through the difficult period.
A University of Michigan Health study found that healthcare professionals offering comprehensive care significantly improved withdrawal outcomes for individuals attempting to detox. This level of care ensures that patients have support for both physical and emotional symptoms.
What Holistic Approaches Are Available For Antidepressant Withdrawal?
Holistic approaches for antidepressant withdrawal include therapies such as acupuncture, yoga, mindfulness-based cognitive therapy, and herbal supplements like omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin B complex. These natural remedies are used to balance physical and emotional health while reducing the severity of withdrawal symptoms.
According to Stanford Medicine, these holistic methods, when combined with a gradual tapering plan, can make the withdrawal process more manageable. They can help provide a sense of balance and reduce discomfort during the process.
How Does Antidepressant Withdrawal Affect Brain Chemistry?
Antidepressant withdrawal can significantly affect brain chemistry, particularly serotonin levels. A sudden drop in serotonin due to rapid tapering or abrupt cessation can lead to severe symptoms like electric shocks, mood swings, and depressive episodes.
The Yale School of Medicine suggests that a slow tapering process helps maintain serotonin levels more evenly, thus preventing dramatic shifts in brain chemicals that could lead to uncomfortable withdrawal symptoms. This gradual process is key to reducing withdrawal difficulties.
Are There Differences In Withdrawal Symptoms Between Short And Long-Acting Antidepressants?
Withdrawal symptoms vary depending on whether an individual is taking short-acting or long-acting antidepressants. Short-acting antidepressants tend to cause more intense withdrawal symptoms, including brain zaps, mood swings, and vivid dreams.
Long-acting antidepressants are generally easier to taper and are less likely to produce severe withdrawal symptoms. The Royal College of Psychiatrists advises individuals to consult healthcare professionals to decide the best strategy based on their specific medication.
What Role Does Medical Detox Play In Antidepressant Withdrawal?
Medical detox is often crucial for individuals experiencing intense withdrawal symptoms or those with a history of substance use disorders. Medical detox provides a supervised setting where healthcare professionals can offer medications to alleviate symptoms and monitor physical health.
Cedars-Sinai emphasizes that a structured detox process reduces the risks associated with abrupt discontinuation and ensures proper care throughout the withdrawal period. This approach can be essential for those at higher risk.
Can Antidepressant Withdrawal Cause Physical Symptoms?
Yes, antidepressant withdrawal can lead to numerous physical symptoms, such as headaches, nausea, dizziness, fatigue, and electric shock sensations. These symptoms can often be as challenging as the psychological symptoms of withdrawal, with many individuals reporting extreme discomfort.
Kaiser Permanente advises patients to seek healthcare support for managing these physical symptoms through a combination of medications and lifestyle adjustments. Effective symptom management can significantly reduce discomfort.
What Are Effective Treatment Options For Antidepressant Discontinuation Syndrome?
Treatment options for antidepressant discontinuation syndrome include a combination of medical intervention, psychological support, and lifestyle changes. Healthcare providers often suggest medications to alleviate severe symptoms and behavioral therapies like one-on-one therapy for psychological symptoms.
Mount Sinai Health System highlights that the severity of withdrawal symptoms significantly decreases with a well-planned and monitored discontinuation strategy. This approach can make the withdrawal process more bearable and minimize complications.
How Can Emotional Symptoms During Antidepressant Withdrawal Be Managed?
Managing emotional symptoms during antidepressant withdrawal, such as irritability, emotional numbness, or mood swings, requires a combination of therapeutic techniques and social support. Counseling services, including family therapy sessions, can help address underlying psychological symptoms and offer a path to recovery.
The American Counseling Association suggests that maintaining a support network and incorporating stress-reduction techniques like meditation and deep breathing can make a significant difference in managing emotional symptoms. This support is essential for emotional well-being during withdrawal.
Is Antidepressant Detoxification A Part Of Recovery From Clinical Depression?
Antidepressant detoxification can be a critical component of the recovery journey for individuals recovering from clinical depression. Detoxification should be approached carefully to prevent withdrawal symptoms and the risk of relapse.
Mayo Clinic emphasizes that detoxification from antidepressants must always be carried out under the guidance of healthcare professionals to ensure safety and reduce the likelihood of a recurrence of depressive symptoms. Supervision is key to ensuring a successful detox.
How Can Withdrawal Symptoms Be Alleviated Naturally During Antidepressant Discontinuation?
Natural methods for alleviating withdrawal symptoms during antidepressant discontinuation include exercise, mindfulness practices, yoga, and dietary supplements. Omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin B complex can be beneficial for supporting brain health during withdrawal.
Cleveland Clinic advises individuals to explore complementary therapies and lifestyle changes alongside professional supervision to manage symptoms effectively without the need for additional medication. Natural remedies can be an effective part of the withdrawal management plan.
How Does Antidepressant Withdrawal Impact Daily Life?
Antidepressant withdrawal can significantly impact daily life, causing symptoms like dizziness, fatigue, vivid dreams, and irritability, which interfere with everyday activities. These symptoms may make it challenging to maintain focus at work or engage in regular social interactions.
The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) Health advises individuals experiencing withdrawal to take necessary measures such as reducing stress, maintaining a structured routine, and seeking professional support to cope with these changes. These steps can help manage the disruptions caused by withdrawal.




