Last updated on December 22nd, 2024 at 09:24 pm
- 1. The Nature of Grief
- 1.1 The Emotional Landscape of Grief
- 1.2 Physical Manifestations of Grief
- 1.3 Cognitive Aspects of Grief
- 2. The Process of Mourning
- 2.1 Cultural Variations in Mourning
- 2.2 Common Mourning Rituals
- 2.3 The Role of Mourning in Healing
- 3. The Interplay Between Grief and Mourning
- 3.1 How Mourning Shapes Grief
- 3.2 How Grief Influences Mourning
- 4. Grief and Mourning Across the Lifespan
- 4.1 Childhood and Adolescence
- 4.2 Adulthood
- 4.3 Later Life
- 5. Complicated Grief and Prolonged Mourning
- 5.1 Understanding Complicated Grief
- 5.2 Risk Factors for Complicated Grief
- 5.3 Interventions for Complicated Grief
- 6. Supporting Others Through Grief and Mourning
- 6.1 Effective Communication
- 6.2 Practical Support
- 6.3 Long-Term Support
- Types of Grief and Their Unique Characteristics
- Stages of Grief: Navigating the Emotional Process
- Anticipatory Grief: A Pre-Loss Emotional Experience
- The Impact on Daily Life and Mental Health Consequences
- Levels of Grief: Variability in Intensity
- The Role of Mourning in Providing Structure and Community Support
- Emotional Reactions and Regressive Behaviors in Grief
- The Role of Mental Health Professionals in the Mourning Journey
- Spirituality and the Grief Process
- Support Systems and Health Care Decisions in Bereavement
- Grief Counseling and Complicated Grief Treatment
- Online Therapy Platforms for Accessible Grief Support
- The Role of the American Journal in Understanding Grief
- Reductions in Distress Through Mourning Rituals
- Types of Grief: Uncomplicated Grief and Its Features
- Imaginary Illnesses and Grief Reactions in Children
- Unfinished Business in Families of Terminally Ill With Cancer
- Grief and Mourning Symbols: Navigating the Signs of Loss
- Grief and Mourning Practices Among Elderly Persons
- Mental Disorders and Elevated Grief Responses
- Grief and Mourning Adaptation Through Creative Outlets
- The Role of Health Care Professionals in Complicated Grief Reaction
- Breast Cancer Prevention and Awareness of Death in Anticipatory Grief
- Grief and Mourning Communities and Support Networks
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What Is The Difference Between Grief And Mourning?
- How Do The Stages Of Grief Relate To Mourning?
- What Are Some Common Examples Of Mourning Practices?
- How Does Complicated Grief Differ From Normal Grief?
- How Can Grief Affect Physical Health?
- What Role Do Cultural Practices Play In Mourning?
- How Can Grief Counseling Help In Coping With Loss?
- What Are Some Healthy Coping Mechanisms For Dealing With Grief?
- How Does Anticipatory Grief Differ From Grief After A Loss?
- How Can Supporting Someone Who Is Grieving Impact One’s Own Emotional Well-being?
- How Does Grief Manifest Differently In Children Compared To Adults?
- What Role Does Spirituality Or Religion Play In The Grieving Process?
- How Can Unresolved Grief Impact Long-term Mental Health?
- What Are Some Cultural Differences In Mourning Practices Around The World?
- How Does Grief Affect Sleep Patterns And What Can Be Done To Improve Sleep During Mourning?
- What Are Some Effective Ways To Support A Grieving Friend Or Family Member?
- How Does Grief Manifest In The Workplace And What Can Employers Do To Support Grieving Employees?
- What Role Do Grief Support Groups Play In The Mourning Process?
- How Does The Concept Of Disenfranchised Grief Relate To Mourning Practices?
- What Is the Difference Between Grief and Mourning?
- How Do Cultural Practices Influence Mourning Rituals?
- Can Mourning Occur Without Grief?
- How Do Mental Health Professionals Support Individuals in Grief and Mourning?
- What Are the Stages of Grief and How Do They Relate to Mourning?
- How Does Anticipatory Grief Differ from Traditional Grief?
- What Are Common Emotional Reactions During the Mourning Process?
- How Can One Differentiate Between Normal Grief and Complicated Grief?
- What Role Do Rituals Play in the Mourning Process?
- How Does Mourning Affect Daily Life and Functioning?
- What Are the Health Implications of Prolonged Grief?
- How Can One Support a Loved One Who Is Mourning?
- What Are the Signs That Professional Help Is Needed During Grief and Mourning?
- What Is the Impact of Mourning on Mental Health?
- How Does Grief Counseling Aid in the Mourning Process?
- What Are the Effects of Anticipatory Grief on Mourning?
- How Does the Mourning Process Differ Across Cultures?
- How Does Mourning Affect Social Relationships?
- What Are the Long-Term Effects of Mourning on Emotional Well-Being?
- How Can Mourning Rituals Facilitate Emotional Recovery?
The experience of loss is a universal aspect of the human condition, touching lives across cultures, ages, and backgrounds. When we lose someone or something significant, we embark on a complex emotional journey that encompasses both grief and mourning.
While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct aspects of the process of coping with loss. Understanding the nuances between grief and mourning can provide valuable insights into the healing process and help individuals navigate the challenging terrain of bereavement.
Let’s discover Grief Vs. Mourning, and learn effective ways to cope with loss. Understand how each affects healing and emotional recovery.
1. The Nature of Grief
Grief is the internal, emotional response to loss. It encompasses a wide range of feelings, thoughts, and physical sensations that arise when we experience a significant loss. Grief is a deeply personal and subjective experience, unique to each individual.
1.1 The Emotional Landscape of Grief
The emotional terrain of grief is vast and varied, often characterized by:
• Sadness: A profound sense of sorrow and emptiness
• Anger: Feelings of frustration, injustice, or abandonment
• Guilt: Regret over unresolved issues or perceived failings
• Fear: Anxiety about the future and coping without the lost person or thing
• Loneliness: A sense of isolation, even when surrounded by others
• Relief: In some cases, especially after a prolonged illness
These emotions often fluctuate, creating what some describe as an “emotional rollercoaster.” It’s important to note that there is no “correct” way to grieve, and individuals may experience these emotions in varying intensities and durations.
1.2 Physical Manifestations of Grief
Grief isn’t confined to emotional experiences; it can also manifest physically:
• Sleep disturbances: Insomnia or oversleeping
• Changes in appetite: Loss of appetite or emotional eating
• Fatigue: Feeling physically drained or lacking energy
• Aches and pains: Headaches, muscle tension, or gastrointestinal issues
These physical symptoms underscore the profound impact grief can have on overall well-being and highlight the importance of self-care during the grieving process.


1.3 Cognitive Aspects of Grief
Grief can significantly affect cognitive functioning:
• Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
• Forgetfulness or feeling mentally “foggy”
• Preoccupation with thoughts of the deceased or the loss
• Questioning of beliefs or searching for meaning
These cognitive changes can be disorienting and may impact daily functioning, emphasizing the need for patience and understanding during the grieving process.
2. The Process of Mourning
While grief represents the internal experience of loss, mourning refers to the external expression of that grief. Mourning is the outward manifestation of our internal emotional state and often involves cultural, religious, or social rituals and practices.
2.1 Cultural Variations in Mourning
Mourning practices vary widely across cultures:
• Western cultures often involve funerals or memorial services
• Some Asian cultures may practice ancestor veneration
• Certain African traditions include elaborate funeral rites lasting several days
• Jewish mourning practices include sitting shiva for seven days
These diverse practices highlight the importance of cultural context in understanding and respecting different mourning traditions.
2.2 Common Mourning Rituals
While specific practices differ, some common elements of mourning include:
• Wearing specific colors (e.g., black in many Western cultures)
• Gathering with family and friends to share memories
• Creating memorials or shrines
• Observing periods of silence or reflection
• Engaging in charitable acts in memory of the deceased
These rituals serve multiple purposes, including honoring the deceased, providing structure during a chaotic time, and fostering community support.
2.3 The Role of Mourning in Healing
Mourning plays a crucial role in the healing process by:
• Providing a structured outlet for grief
• Facilitating social support and connection
• Helping to make the loss “real” and tangible
• Allowing for the expression of emotions in a socially acceptable manner
• Creating lasting memories and tributes to the deceased
Engaging in mourning practices can help individuals move through their grief and begin to integrate the loss into their lives.
3. The Interplay Between Grief and Mourning
While grief and mourning are distinct processes, they are deeply interconnected and often influence each other in significant ways.
3.1 How Mourning Shapes Grief
Mourning practices can impact the grieving process by:
• Providing a framework for expressing and processing emotions
• Creating opportunities for social support and connection
• Offering rituals that can bring comfort and meaning
• Helping to mark the passage of time and transitions in the grieving process
Engaging in mourning activities can sometimes intensify grief in the short term but may ultimately facilitate healing and acceptance.


3.2 How Grief Influences Mourning
The internal experience of grief can shape how individuals engage in mourning:
• The intensity of grief may influence the extent of mourning activities
• Personal beliefs and values shaped by grief may impact chosen mourning practices
• Grief-related emotions may affect one’s ability or desire to participate in certain rituals
Understanding this interplay can help individuals and their support systems navigate the complex landscape of loss more effectively.
4. Grief and Mourning Across the Lifespan
The experience of grief and mourning can vary significantly across different life stages, reflecting changing cognitive abilities, social roles, and life experiences.
4.1 Childhood and Adolescence
Children and adolescents may experience grief and mourning differently:
• Limited understanding of death’s permanence in young children
• Intermittent grief reactions, with periods of seeming normalcy
• Potential for delayed grief responses as cognitive abilities develop
• Impact on identity formation and future outlook in adolescents
Supporting young people through loss requires age-appropriate explanations and interventions.
4.2 Adulthood
Adult grief and mourning experiences may be influenced by:
• Multiple roles and responsibilities that compete with grieving
• More complex relationships and unresolved issues with the deceased
• Greater life experience and potentially more developed coping skills
• Societal expectations about “appropriate” grieving
Adults may benefit from finding ways to balance their grief with ongoing life demands.
4.3 Later Life
Older adults face unique challenges in grief and mourning:
• Cumulative losses over a lifetime
• Reduced social support networks
• Physical limitations that may impact participation in mourning rituals
• Existential questions about mortality and life meaning
Supporting older adults in grief may involve addressing both emotional and practical needs.


5. Complicated Grief and Prolonged Mourning
While grief and mourning are normal responses to loss, sometimes these processes become prolonged or complicated, leading to significant distress and impairment.
5.1 Understanding Complicated Grief
Complicated grief is characterized by:
• Persistent, intense yearning for the deceased
• Difficulty accepting the reality of the loss
• Avoidance of reminders of the loss
• Inability to engage in daily activities or find joy in life
• Symptoms persisting for an extended period (typically more than 6-12 months)
Recognizing the signs of complicated grief is crucial for providing appropriate support and intervention.
5.2 Risk Factors for Complicated Grief
Several factors may increase the risk of developing complicated grief:
• Sudden or traumatic loss
• Loss of a child or spouse
• History of mental health issues or substance abuse
• Lack of social support
• Multiple concurrent losses
Awareness of these risk factors can help identify individuals who may need additional support.
5.3 Interventions for Complicated Grief
Specialized interventions for complicated grief may include:
• Cognitive-behavioral therapy focused on grief
• Narrative therapy to help reconstruct meaning after loss
• Prolonged exposure therapy for traumatic losses
• Medication in some cases, particularly for co-occurring depression
Professional help can be crucial in navigating the challenges of complicated grief.
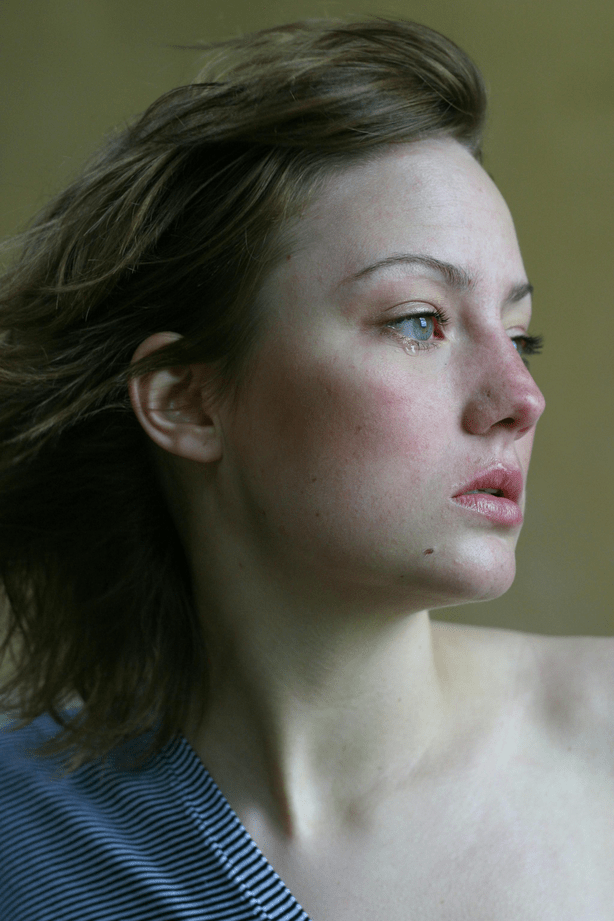
6. Supporting Others Through Grief and Mourning
Providing support to those experiencing loss is a vital aspect of human connection and community. Effective support requires empathy, patience, and understanding.
6.1 Effective Communication
Key principles for communicating with grieving individuals include:
• Listening without judgment
• Avoiding platitudes or attempts to “fix” the grief
• Validating emotions and experiences
• Being present and available, even in silence
Effective communication can help grieving individuals feel heard and supported.
6.2 Practical Support
Offering practical assistance can be invaluable:
• Helping with daily tasks or errands
• Assisting with funeral or memorial arrangements
• Providing meals or childcare
• Offering to accompany them to appointments or events
Practical support can alleviate some of the burdens that accompany loss.
6.3 Long-Term Support
Remember that grief doesn’t have a set timeline:
• Continue to check in over time
• Be mindful of significant dates or anniversaries
• Respect individual grieving styles and needs
• Encourage professional help if signs of complicated grief emerge
Ongoing support can make a significant difference in the long-term healing process.
Types of Grief and Their Unique Characteristics
There are various types of grief that individuals may experience. Each type has distinct features and impacts.
Disenfranchised grief arises when a loss is not openly acknowledged or socially supported. This can complicate the mourning process.
Traumatic grief results from sudden, unexpected loss. It can include severe emotional reactions and heightened feelings of grief.
Understanding these different grief types helps in recognizing diverse reactions to loss. It also assists in tailoring support appropriately.
Stages of Grief: Navigating the Emotional Process
The stages of grief refer to a series of emotional states that individuals typically pass through. This emotional process includes denial, anger, bargaining, depression, and acceptance.
Not everyone experiences these stages in a linear manner. Some may revisit stages or skip others altogether.
The complexity of the normal grieving process is often highlighted by these variations. Mental health professionals utilize this understanding to guide individuals through the emotional pain of loss.


Anticipatory Grief: A Pre-Loss Emotional Experience
Anticipatory grief occurs when someone expects an imminent loss, such as during a loved one’s terminal illness. It allows individuals to begin processing their feelings of loss before it occurs.
This type of grief can potentially reduce the intensity of the pain of grief after the actual death. Anticipatory grief is particularly relevant in situations involving advanced cancer.
Families often start grieving before the person’s passing. This early grieving can be both helpful and challenging.
The Impact on Daily Life and Mental Health Consequences
Grief often affects daily life, with individuals struggling to maintain routines. Symptoms such as poor sleep, fatigue, or lack of focus are common.
These symptoms can lead to negative health consequences. If left unaddressed, they can result in major depression or other mental disorders.
Seeking help from health care professionals is often beneficial. Grief counseling can also play a crucial role in managing these difficulties.
Levels of Grief: Variability in Intensity
The levels of grief experienced can vary significantly. Some individuals experience minimal grief reaction, while others face intense prolonged grief disorder.
For some, the response to loss may be subdued, such as absent grief. This is where individuals show little outward emotion.
The outward expression does not always align with the internal experience. This can be confusing for those around the grieving person.
Prolonged grief disorder, however, can significantly impact one’s ability to function. It often requires targeted interventions such as complicated grief treatment.
The Role of Mourning in Providing Structure and Community Support
The mourning process provides a structured way for individuals to navigate the chaos of loss. Rituals like funerals and memorials offer opportunities for an outward expression of grief.
Mourning rituals foster a sense of shared experience. They are vital in integrating the loss into one’s life.
Receiving social support is crucial for long-term recovery. Participating in communal mourning activities helps provide this support.
Emotional Reactions and Regressive Behaviors in Grief
Grief can provoke intense emotional reactions, including regressive behaviors. These may include withdrawing from social connections or reverting to previously comforting habits.
In children, these reactions may involve magical thinking. They may believe they can reverse death with magical powers.
Adults may also experience elevated grief responses. This could include aggressive behaviors or fear of rejection due to the profound sense of vulnerability.


The Role of Mental Health Professionals in the Mourning Journey
Mental health professionals play a critical role in the grief and mourning process. They offer tools and strategies to cope with the emotional pain of loss.
Techniques like grief therapy and cognitive restructuring are helpful. They help in managing feelings about grief and mitigating negative consequences.
Professionals also guide those experiencing suicidal ideation. They assist individuals with symptoms of depression towards recovery and resilience American Psychological Association.
Spirituality and the Grief Process
Grief and mourning are often influenced by spiritual beliefs. Many find comfort in regular church attendance or other spiritual practices.
These practices provide a framework for making sense of the loss. Spirituality can offer solace, resilience, and a sense of meaning.
Resources from organizations like the American Society of Clinical Oncology emphasize the importance of spirituality. It is a key element in providing emotional comfort during grief.
Support Systems and Health Care Decisions in Bereavement
Building effective grief and mourning support systems is essential. Friends, family, health care professionals, and community networks can offer emotional and practical assistance.
Decisions surrounding end-of-life care often arise during bereavement. Choosing a health proxy or arranging power of attorney can be challenging.
Utilizing resources like Visuals Online may assist. It helps in better understanding medical options during these challenging times.
Grief Counseling and Complicated Grief Treatment
Grief counseling offers targeted support for those struggling with grief symptoms that hinder daily life. For individuals dealing with prolonged grief disorder, professional intervention is necessary.
Complicated grief treatment through a qualified health professional can be instrumental. This treatment may include cognitive-behavioral strategies, exposure therapy, or medication.
Conditions like major depression often co-occur with prolonged grief. Effective interventions are outlined by the National Cancer Institute’s Cancer Information Summaries.


Online Therapy Platforms for Accessible Grief Support
Online therapy platforms provide a convenient option for those in need of support. They can connect individuals to health care professionals.
These platforms offer flexible and accessible treatment options for grief and mourning symptoms. They are particularly helpful for those experiencing disenfranchised grief.
For those unable to attend in-person sessions, these services are valuable. Many are covered by insurance coverage, reducing financial barriers.
The Role of the American Journal in Understanding Grief
Research published in reputable journals like the American Journal provides valuable insights into the grief and mourning process. These studies contribute to understanding the effectiveness of various treatments.
Grief therapy and best practices for navigating complicated grief reactions are highlighted. Springer Publishing Company features empirical evidence and formal guidelines for treating grief effectively.
Reductions in Distress Through Mourning Rituals
Structured mourning activities can lead to reductions in distress. Memorial services provide tangible ways to express emotional pain.
These rituals allow for communal reaction to loss. This connection is crucial in the grief and mourning process.
Engaging in structured activities acknowledges the death from life. It provides a sense of closure and begins the healing process.
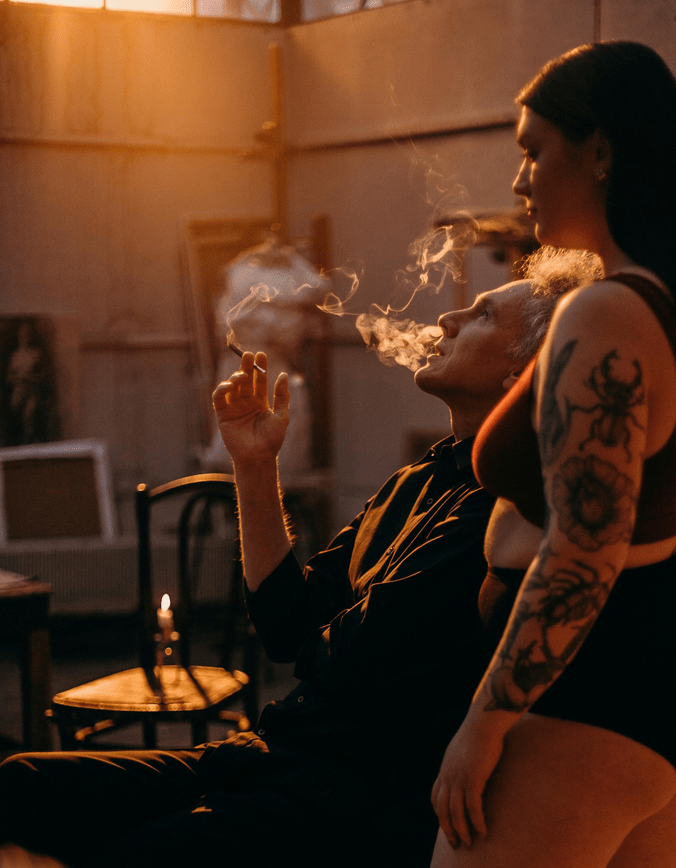
Types of Grief: Uncomplicated Grief and Its Features
Uncomplicated grief is considered a normal grieving response. It allows individuals to gradually adapt to the loss over time.
Unlike prolonged grief disorder, this type of grief does not require medical intervention. The mourning process unfolds naturally.
Emotions experienced during uncomplicated grief often align with common grief reactions. Though painful, these reactions do not hinder the ability to regain balance in daily life.
Understanding these variations aids in distinguishing between healthy grieving and more severe complications. This distinction is essential for providing the appropriate support.
Imaginary Illnesses and Grief Reactions in Children
Children may exhibit imaginary illnesses as a response to grief. This reflects their struggle to articulate emotional pain.
The manifestation of imaginary illnesses stems from difficulty expressing feelings of loss. Children may not have the words to convey their emotions.
Magical thinking in children is also common during grief. They may believe they can influence events or even bring back the dead person.
Such behaviors highlight the unique way in which children process separation. It underscores the importance of age-appropriate support for grieving children.
Unfinished Business in Families of Terminally Ill With Cancer
Grief can often be complicated by unfinished business between the bereaved and the deceased. This is especially true in cases involving terminal illness.
Unspoken conversations and untaken actions can intensify emotional reactions. They complicate the healing process.
Addressing unresolved issues through counseling or reflection can mitigate prolonged grief disorder symptoms. It helps ease the transition from grief towards acceptance.
This is particularly relevant in advanced cancer scenarios. Support from resources like the National Cancer Institute can assist families in these situations.


Grief and Mourning Symbols: Navigating the Signs of Loss
Symbols play an essential role in the grief and mourning process. They provide visual representation of the emotional journey.
Examples include wearing specific grief and mourning colors or keeping a keepsake. These symbols act as tangible reminders of the deceased person.
These symbols are part of many cultural mourning practices. They help individuals externalize their grief and acknowledge their loss.
Outward expression of grief can be instrumental in coping. Symbols help foster shared connections during communal mourning events.
Grief and Mourning Practices Among Elderly Persons
Elderly persons often face unique grief experiences. Cumulative losses over a lifetime contribute to the challenge.
Physical limitations may prevent active participation in traditional mourning rituals. This can further exacerbate a sense of isolation.
Support systems that accommodate physical challenges are crucial. Accessible ceremonies or virtual gatherings can be helpful.
Adjustments ensure elderly individuals remain connected to the community. They provide necessary support throughout the mourning process.
Mental Disorders and Elevated Grief Responses
The experience of grief can sometimes trigger mental disorders. Symptoms can remain intense for extended periods.
Conditions like major depression or prolonged grief disorder are more likely in individuals facing traumatic loss. Elevated grief responses interfere with one’s ability to function.
Intervention by health care professionals is crucial. Their support aids in managing intense reactions and stabilizing mental health.
Grief and Mourning Adaptation Through Creative Outlets
Engaging in creative outlets can be therapeutic. Grief and mourning art or writing provide personal ways to express grief.
Creative activities serve as a bridge between internal emotions and outward expression. They offer a channel for releasing pent-up feelings.
Individuals often find meaning through these creative acts. This sense of purpose aids in emotional healing and adaptation to loss.
Creative practices are essential parts of grief therapy. They encourage individuals to work through grief in a constructive manner.
The Role of Health Care Professionals in Complicated Grief Reaction
Health care professionals play a vital role in addressing complicated grief reaction. They assess whether grief has extended beyond normal limits.
When grief begins to interfere with daily functioning, complicated grief treatment becomes necessary. This includes grief counseling and other targeted interventions.
Medications may be used, particularly when symptoms like pessimistic thinking or suicidal ideation are present. Professionals provide structured guidance to navigate the emotional process.
Support from health care professionals promotes resilience. Their intervention aids in coping with significant loss effectively.


Breast Cancer Prevention and Awareness of Death in Anticipatory Grief
Facing the loss of a loved one due to breast cancer brings heightened awareness of death. It prompts discussions around prevention and health.
Anticipatory grief allows family members to address concerns proactively. Increased vigilance in breast cancer prevention often follows.
The American Cancer Society provides cancer information summaries to help individuals make informed decisions. These resources guide through medical, emotional, and preventive aspects of loss.
Preparedness is key in navigating anticipatory grief. It fosters a sense of control in the midst of uncertainty.
Grief and Mourning Communities and Support Networks
Grief and mourning communities play a crucial role in support. Peer support groups provide invaluable spaces for sharing experiences.
Online and in-person groups offer emotional support. Connecting with others helps individuals realize they are not alone.
Grief and mourning online forums are also beneficial. They offer a sense of community for those who may not have local support.
Attending grief and mourning workshops can be transformative. These connections provide understanding and empathy that foster the mourning journey.
Shared experiences strengthen the support network. This communal approach helps in healing and provides a sense of belonging.
From Embrace Inner Chaos to your inbox
Transform your Chaos into authentic personal growth – sign up for our free weekly newsletter! Stay informed on the latest research advancements covering:
Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD)
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Difference Between Grief And Mourning?
Grief and mourning are closely related but distinct aspects of dealing with loss. The Recovery Village explains that grief refers to the internal thoughts and feelings experienced after a loss, such as sadness, anger, or longing. Mourning, on the other hand, is the outward expression of these feelings through behaviors and actions.
Grief is a deeply personal and often private experience, varying greatly from person to person. It encompasses the emotional turmoil one goes through when facing a significant loss. Mourning, however, is more public and often influenced by cultural practices and social norms.
The process of grief can be ongoing and may not have a specific time frame, while mourning often involves specific rituals or customs that help individuals navigate their grief journey. Understanding this difference can be crucial in recognizing and respecting diverse ways people cope with loss.
How Do The Stages Of Grief Relate To Mourning?
The stages of grief, originally proposed by Elisabeth Kübler-Ross, are often associated with both grief and mourning processes. HelpGuide outlines these stages as denial, anger, bargaining, depression, and acceptance. However, it’s important to note that these stages are not linear and don’t necessarily apply to everyone.
In the context of mourning, these stages may manifest in different ways. For example, denial might be expressed through avoiding funeral arrangements, while anger could be shown through public displays of frustration. The bargaining stage might involve making promises or deals with a higher power, often as part of religious or spiritual practices.
Depression and acceptance, the later stages, often involve more internal processing but can still be reflected in mourning behaviors. For instance, depression might lead to withdrawal from social activities, while acceptance could be demonstrated through participating in memorial services or creating tributes to the deceased.
What Are Some Common Examples Of Mourning Practices?
Mourning practices vary widely across cultures and individuals, but there are some common examples that many people engage in. Thriveworks mentions several mourning activities that help individuals process their grief and honor the deceased.
One of the most common mourning practices is attending or organizing a funeral or memorial service. These events provide a structured way to say goodbye and often involve sharing memories of the deceased. Wearing black clothing is another traditional mourning practice in many Western cultures, symbolizing the somber nature of the occasion.
Other examples include creating memory books or scrapbooks, writing letters to the deceased, or establishing memorials in their honor. Some people may engage in charitable activities or volunteer work in memory of their loved one. These external expressions of grief serve not only as a way to process emotions but also as a means of keeping the memory of the deceased alive.
How Does Complicated Grief Differ From Normal Grief?
Complicated grief, also known as prolonged grief disorder, is a condition where acute grief symptoms persist for an extended period and interfere significantly with daily functioning. PMC provides insights into how complicated grief differs from normal grief in both intensity and duration.
In normal grief, the acute pain of loss gradually subsides over time, allowing the bereaved to adapt to life without their loved one. While sadness may persist, it becomes less overwhelming, and the individual can engage in daily activities and find moments of joy. Complicated grief, however, is characterized by intense longing, preoccupation with the deceased, and difficulty accepting the reality of the loss.
People experiencing complicated grief often struggle to move forward with their lives, feeling stuck in their grief. They may experience persistent feelings of emptiness, have trouble maintaining relationships, or lose interest in previously enjoyable activities. Unlike normal grief, which tends to improve with time, complicated grief requires professional intervention to help the individual process their loss and regain functionality.
How Can Grief Affect Physical Health?
Grief is not just an emotional experience; it can have significant impacts on physical health as well. HelpGuide explains that the stress and emotional turmoil of grief can manifest in various physical symptoms and health issues.
Common physical manifestations of grief include fatigue, sleep disturbances, and changes in appetite. Some people may experience headaches, muscle tension, or digestive problems. The immune system can be compromised during periods of intense grief, making individuals more susceptible to illnesses.
In more severe cases, grief can exacerbate existing health conditions or contribute to the development of new ones. For example, studies have shown an increased risk of cardiovascular problems in bereaved individuals, particularly in the early stages of grief. It’s crucial for those experiencing grief to pay attention to their physical health and seek medical attention if they notice persistent or concerning symptoms.
What Role Do Cultural Practices Play In Mourning?
Cultural practices play a significant role in shaping mourning behaviors and rituals. The Recovery Village highlights how different cultures have unique ways of expressing grief and honoring the deceased, which can greatly influence the mourning process.
In some cultures, mourning is a highly structured process with specific timelines and rituals. For example, certain Jewish traditions involve a week-long period of intense mourning called shiva, followed by less intense periods of mourning over the course of a year. In contrast, some Native American tribes may have mourning periods that last for several years.
The way death is viewed culturally also impacts mourning practices. Some cultures celebrate death as a transition rather than an ending, leading to more festive mourning rituals. Others may have strict rules about how the deceased should be treated and remembered. Understanding these cultural differences is crucial in providing appropriate support to bereaved individuals from diverse backgrounds.
How Can Grief Counseling Help In Coping With Loss?
Grief counseling can be an invaluable resource for individuals struggling to cope with loss. Thriveworks explains that grief counselors are trained professionals who can provide support and guidance through the grieving process.
One of the primary benefits of grief counseling is that it offers a safe, non-judgmental space to express emotions and process the loss. Counselors can help individuals understand their grief reactions and validate their feelings, which is particularly helpful when someone feels their grief is abnormal or prolonged.
Grief counselors can also provide practical coping strategies tailored to the individual’s needs. These may include relaxation techniques, journaling exercises, or ways to honor the deceased’s memory. Additionally, counseling can help address any complicated grief symptoms, preventing them from developing into more serious mental health issues.
What Are Some Healthy Coping Mechanisms For Dealing With Grief?
Developing healthy coping mechanisms is crucial for navigating the grief journey. HelpGuide offers several strategies that can help individuals process their grief in a healthy manner.
One important coping mechanism is acknowledging and accepting one’s feelings. This involves allowing oneself to feel the full range of emotions associated with grief, rather than trying to suppress or avoid them. Expressing these feelings through talking, writing, or creative activities can be particularly beneficial.
Maintaining connections with others is another vital coping strategy. This could involve reaching out to friends and family for support, joining a grief support group, or engaging in community activities. Physical self-care, including regular exercise, healthy eating, and adequate sleep, is also crucial in managing the stress of grief.
How Does Anticipatory Grief Differ From Grief After A Loss?
Anticipatory grief refers to the grief experienced before an impending loss, often in cases of terminal illness or other situations where death is expected. PMC provides insights into how this type of grief differs from post-loss grief.
One key difference is that anticipatory grief occurs while the person is still alive, allowing for continued interaction and potential closure. This can involve saying goodbyes, resolving conflicts, or expressing love and appreciation. However, it can also be complicated by the uncertainty of when the loss will occur and the stress of caregiving responsibilities.
Anticipatory grief can sometimes make the post-loss grieving process easier, as some emotional processing has already occurred. However, it doesn’t necessarily reduce the intensity of grief after the loss. In some cases, people may feel guilty for grieving before the person has died, adding another layer of emotional complexity to the experience.
How Can Supporting Someone Who Is Grieving Impact One’s Own Emotional Well-being?
Supporting someone who is grieving can have significant impacts on one’s own emotional well-being. The Recovery Village discusses how being a support system for someone in grief can be both rewarding and challenging.
Providing support can foster a sense of purpose and connection, potentially strengthening the relationship with the grieving person. It can also lead to personal growth and increased empathy. However, it’s important to recognize that supporting someone through grief can be emotionally taxing.
Helpers may experience secondary grief, where they absorb some of the emotional pain of the person they’re supporting. This can lead to feelings of sadness, helplessness, or frustration. It’s crucial for supporters to practice self-care and set boundaries to prevent emotional burnout. Seeking support for oneself, whether through friends, family, or professional counseling, can be beneficial in maintaining one’s own emotional well-being while supporting others.
How Does Grief Manifest Differently In Children Compared To Adults?
Grief can manifest quite differently in children compared to adults, largely due to their developmental stage and limited life experience. HelpGuide provides insights into these differences and how to support grieving children.
Children’s grief often comes in waves rather than as a constant state. They may seem fine one moment and deeply sad the next. Unlike adults, children may not have the vocabulary to express their complex emotions, leading to behavioral changes such as aggression, withdrawal, or regression in developmental milestones.
Children’s understanding of death also evolves with age. Younger children may not grasp the permanence of death, leading to repeated questions about when the deceased will return. Older children and teenagers may grapple with existential questions and fears about their own mortality. It’s crucial to provide age-appropriate explanations and support, allowing children to grieve in their own way and at their own pace.
What Role Does Spirituality Or Religion Play In The Grieving Process?
Spirituality and religion can play a significant role in the grieving process for many individuals. Thriveworks discusses how spiritual beliefs can influence one’s approach to loss and mourning.
For many, spiritual or religious beliefs provide a framework for understanding death and the afterlife, which can offer comfort and hope during the grieving process. Religious rituals and practices, such as funeral services or prayer, can provide structure and community support during a time of loss.
Spirituality can also offer coping mechanisms, such as meditation or mindfulness practices, that help individuals process their grief. Some find solace in the belief that their loved one is in a better place or that they will be reunited in the afterlife. However, it’s important to note that grief can also challenge one’s faith, leading to spiritual struggles or crises that may require additional support.
How Can Unresolved Grief Impact Long-term Mental Health?
Unresolved grief, if left unaddressed, can have significant long-term impacts on mental health. PMC provides insights into the potential consequences of grief that persists without resolution.
One of the most common outcomes of unresolved grief is the development of complicated grief, where acute grief symptoms persist for an extended period. This can lead to chronic depression, anxiety disorders, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), especially if the loss was sudden or traumatic.
Unresolved grief can also manifest in physical symptoms, such as chronic pain or weakened immune function. It may impact relationships, as the grieving individual might struggle to form new connections or maintain existing ones. In some cases, unresolved grief can lead to substance abuse as a coping mechanism. Recognizing these potential impacts underscores the importance of addressing grief actively and seeking professional help when needed.
What Are Some Cultural Differences In Mourning Practices Around The World?
Mourning practices vary widely across different cultures, reflecting diverse beliefs about death, the afterlife, and the proper way to honor the deceased. The Recovery Village highlights some of these cultural differences in mourning.
In many Western cultures, mourning often involves somber gatherings dressed in black. However, in some cultures, white is the color of mourning. For example, in parts of East Asia, white represents purity and rebirth. In contrast, some African and South American cultures have vibrant, celebratory funeral practices, viewing death as a transition to be honored rather than mourned.
The duration of mourning also varies. Some cultures have prescribed mourning periods, such as the Jewish tradition of sitting shiva for seven days. Others, like some Native American tribes, may observe mourning practices for years. Understanding these cultural differences is crucial for providing culturally sensitive support to bereaved individuals from diverse backgrounds.
How Does Grief Affect Sleep Patterns And What Can Be Done To Improve Sleep During Mourning?
Grief can significantly disrupt sleep patterns, leading to insomnia, nightmares, or excessive sleeping. HelpGuide provides insights into how grief affects sleep and offers strategies for improving sleep quality during the mourning process.
During grief, the mind often becomes preoccupied with thoughts of the deceased or ruminations about the loss, making it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep. Stress hormones released during grief can also interfere with the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. Some individuals may experience vivid dreams or nightmares about their loved one.
To improve sleep during mourning, establishing a consistent sleep routine can be helpful. This includes going to bed and waking up at the same time each day. Creating a relaxing bedtime ritual, such as reading or listening to calming music, can also promote better sleep. If sleep problems persist, seeking help from a healthcare provider or sleep specialist may be necessary.
What Are Some Effective Ways To Support A Grieving Friend Or Family Member?
Supporting a grieving friend or family member can be challenging, but there are several effective ways to offer comfort and assistance. Thriveworks provides guidance on how to be a supportive presence for someone who is mourning.
One of the most important things is to simply be present and available. This might mean listening without judgment, offering a shoulder to cry on, or just sitting in silence together. Avoid trying to “fix” their grief or offering platitudes like “they’re in a better place now.”
Practical support can also be invaluable. This could involve helping with daily tasks, preparing meals, or assisting with funeral arrangements. Remember that grief doesn’t end after the funeral, so continuing to check in and offer support in the weeks and months following the loss is crucial.
How Does Grief Manifest In The Workplace And What Can Employers Do To Support Grieving Employees?
Grief can significantly impact an individual’s work performance and overall workplace dynamics. The Recovery Village discusses how grief manifests in the workplace and what employers can do to support grieving employees.
In the workplace, grief may manifest as decreased productivity, difficulty concentrating, increased absenteeism, or emotional outbursts. Grieving employees may struggle with motivation or find it challenging to engage in workplace social interactions. These reactions can persist for months or even years after a loss.
Employers can support grieving employees by offering flexible work arrangements, such as adjusted schedules or remote work options. Providing access to grief counseling services through employee assistance programs can be beneficial. Creating a supportive work environment where employees feel comfortable discussing their loss and needs is also crucial. Training managers on how to handle grief in the workplace can ensure more consistent and compassionate support for bereaved employees.
What Role Do Grief Support Groups Play In The Mourning Process?
Grief support groups can play a crucial role in the mourning process, offering a unique form of support that complements individual coping strategies and professional therapy. HelpGuide explains the benefits of participating in grief support groups.
One of the primary advantages of support groups is the opportunity to connect with others who are going through similar experiences. This can help reduce feelings of isolation and normalize grief reactions. Hearing others’ stories and coping strategies can provide new perspectives and ideas for managing one’s own grief.
Support groups also offer a safe space to express emotions and share memories of the deceased. For some, it may be easier to open up about their grief with strangers who understand the experience than with close friends or family. Additionally, participating in a support group can provide a sense of purpose and the opportunity to help others, which can be healing in itself.
How Does The Concept Of Disenfranchised Grief Relate To Mourning Practices?
Disenfranchised grief refers to grief that is not openly acknowledged, socially validated, or publicly mourned. PMC discusses how this concept relates to mourning practices and its impact on the grieving process.
Disenfranchised grief often occurs in situations where the loss is not recognized as significant by society. Examples include the death of an ex-spouse, a miscarriage, the loss of a pet, or the death of someone with whom the griever had a socially unacceptable relationship. In these cases, individuals may not feel entitled to mourn openly or may not receive the same level of support as those experiencing more socially recognized losses.
This lack of social validation can complicate the mourning process, leading to feelings of shame, guilt, or anger. It may prevent individuals from engaging in traditional mourning practices or seeking support, potentially prolonging the grief process. Recognizing and validating disenfranchised grief is crucial for providing appropriate support and allowing individuals to mourn their losses fully.
What Is the Difference Between Grief and Mourning?
Grief refers to the internal experience of loss. It encompasses the thoughts and feelings that arise after losing someone or something significant.
This emotional process includes a range of reactions such as sadness, anger, guilt, and despair. Mourning, on the other hand, is the outward expression of grief.
It involves the rituals, customs, and behaviors through which individuals and communities express their sorrow. These practices help them begin to process the loss.
These mourning practices can vary widely across different cultures and religions (Psych Central).
How Do Cultural Practices Influence Mourning Rituals?
Cultural practices significantly shape mourning rituals. They dictate how grief is expressed publicly.
For instance, some cultures have specific ceremonies, dress codes, or periods of mourning. These customs are observed to honor the deceased.
These rituals provide a structured way for individuals to express their grief. They also facilitate the healing process by offering communal support (LoveToKnow).
Can Mourning Occur Without Grief?
While grief and mourning are closely linked, mourning can occur without the deep emotional experience of grief. This may happen when individuals participate in mourning rituals due to societal or familial expectations.
They may not personally feel the profound emotions associated with grief. This distinction highlights that mourning is the external expression, which may not always align with one’s internal emotional state (LoveToKnow).


How Do Mental Health Professionals Support Individuals in Grief and Mourning?
Mental health professionals play a vital role in supporting individuals through grief. They provide a safe space for individuals to express their feelings.
They help individuals understand the grieving process and offer coping strategies to manage emotional pain. Therapists also assist in addressing complicated grief.
Complicated grief involves a prolonged or debilitating mourning process. Mental health professionals ensure individuals can navigate their loss in a healthy manner (HelpGuide).
What Are the Stages of Grief and How Do They Relate to Mourning?
The stages of grief include denial, anger, bargaining, depression, and acceptance. They describe the internal emotional journey individuals may experience after a loss.
Mourning is the external process that may accompany these stages. It involves actions and rituals that reflect one’s internal state.
For example, during the acceptance stage, an individual might hold a memorial service. This is a way to honor the deceased and find closure (Cleveland Clinic).
How Does Anticipatory Grief Differ from Traditional Grief?
Anticipatory grief occurs when individuals begin to grieve before an impending loss. This often happens when a loved one is diagnosed with a terminal illness.
This type of grief allows individuals to prepare emotionally for the loss. It can potentially ease the mourning process after the loss occurs.
Traditional grief begins after the loss has happened. It encompasses both the emotional and mourning processes that follow the event (Thriveworks).
What Are Common Emotional Reactions During the Mourning Process?
During the mourning process, individuals may experience a range of emotional reactions. These include sadness, anger, guilt, anxiety, and even relief.
These emotions are part of the natural response to loss. They can vary in intensity and duration.
Acknowledging and expressing these feelings through mourning rituals can aid in the healing process. This helps individuals cope more effectively with their emotions (HelpGuide).
How Can One Differentiate Between Normal Grief and Complicated Grief?
Normal grief involves a range of emotions that gradually diminish over time. This allows individuals to resume daily activities.
Complicated grief, however, is characterized by intense, prolonged symptoms. These symptoms interfere with daily life and may require professional intervention.
Recognizing the signs of complicated grief is crucial. Persistent yearning for the deceased or difficulty accepting the loss are indicators to seek support (Verywell Health).
What Role Do Rituals Play in the Mourning Process?
Rituals play a significant role in the mourning process. They provide structure and a sense of community.
They offer a way to honor the deceased and express emotions. Rituals also provide an opportunity to receive support from others.
Engaging in rituals, such as funerals or memorial services, can facilitate the expression of grief. This helps individuals transition to life after loss (LoveToKnow).
How Does Mourning Affect Daily Life and Functioning?
Mourning can significantly impact daily life. It affects one’s ability to concentrate, perform routine tasks, and engage in social activities.
The emotional toll of mourning may lead to physical symptoms like fatigue. Changes in appetite are also common.
Over time, as individuals process their grief, they find ways to adapt. They gradually integrate the loss into their lives and resume normal activities (HelpGuide).
What Are the Health Implications of Prolonged Grief?
Prolonged grief, also known as complicated grief, can have serious health implications. It includes increased risk of depression, anxiety, and physical health issues such as heart disease.
Prolonged grief may lead to difficulties in maintaining relationships. It also affects one’s ability to fulfill daily responsibilities.
Seeking support from mental health professionals is essential. Addressing prolonged grief can mitigate its negative health consequences (Verywell Health).
How Can One Support a Loved One Who Is Mourning?
Supporting a loved one who is mourning involves offering a listening ear. Expressing empathy and respecting their grieving process is important.
Encouraging them to share memories and express feelings can be beneficial. It’s also essential to be patient and understanding.
Recognizing that mourning is a personal journey is crucial. Each individual’s experience may vary, and support must be tailored accordingly (HelpGuide).
What Are the Signs That Professional Help Is Needed During Grief and Mourning?
Signs that professional help may be needed include persistent hopelessness. Inability to perform daily tasks or withdrawal from social interactions are also indicators.
Thoughts of self-harm are a serious concern. If grief leads to major depression or prolonged difficulty in coping, professional support is vital.
Mental health professionals can provide crucial support. They offer coping strategies to navigate through the complex emotions of grief (HelpGuide).
What Is the Impact of Mourning on Mental Health?
Mourning can have a significant impact on mental health. It often triggers symptoms of anxiety and depression.
During this time, individuals may experience poor sleep and changes in appetite. Increased emotional distress is also common.
Mental health professionals can assist by providing grief counseling. This helps individuals navigate their emotions and find effective coping mechanisms (Psych Central).
How Does Grief Counseling Aid in the Mourning Process?
Grief counseling provides a supportive environment for individuals. It allows them to discuss their feelings of loss and develop coping mechanisms.
Counselors use various techniques to help individuals understand their grief. They address the effects of grief on daily life and provide tools to manage it.
Through the therapeutic process, people can begin to accept their loss. They learn to reduce emotional distress and find new meaning after the death of a loved one (Thriveworks).
What Are the Effects of Anticipatory Grief on Mourning?
Anticipatory grief occurs before an expected loss. It can affect how individuals mourn after the actual loss.
It may provide some emotional preparation, reducing the initial shock. This can ease the mourning process for some individuals.
However, anticipatory grief can also intensify feelings of sorrow. This may make the actual loss even more challenging to cope with (Verywell Health).
How Does the Mourning Process Differ Across Cultures?
The mourning process varies significantly across cultures. It is influenced by religious beliefs, traditions, and societal norms.
In some cultures, mourning involves a highly structured set of rituals. This can include wearing specific clothing or observing a defined mourning period.
These practices help individuals express their grief. They also provide a sense of connection to their community, thereby facilitating emotional healing (LoveToKnow).
How Does Mourning Affect Social Relationships?
Mourning can put a strain on social relationships. Individuals may withdraw or find it difficult to relate to others who have not experienced a similar loss.
The emotional burden of mourning can make it challenging to maintain friendships. Family connections may also be affected.
However, shared mourning rituals and open communication can strengthen these relationships. They provide mutual support and help individuals feel less isolated (HelpGuide).
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Mourning on Emotional Well-Being?
Long-term effects of mourning can include both positive and negative outcomes. Prolonged grief may lead to symptoms of depression and emotional withdrawal.
Successfully navigating the mourning process can result in personal growth. It often fosters resilience and an increased appreciation for life.
Seeking support and engaging in meaningful mourning rituals are beneficial. These actions enhance emotional recovery and contribute to overall well-being (Psych Central).
How Can Mourning Rituals Facilitate Emotional Recovery?
Mourning rituals provide an opportunity for individuals to process grief. They help individuals find closure after a significant loss.
Activities such as funerals and memorial services create a space for expressing grief. These rituals also honor the deceased and provide communal support.
Engaging in these rituals can help individuals transition through their grief. They play an essential role in beginning the journey of emotional recovery (LoveToKnow).




