Last updated on December 18th, 2024 at 03:18 am
- Types of Addiction
- Substance Use Disorders
- Behavioral Addictions
- Co-Occurring Disorders
- Enabling Behaviors
- Global Statistics
- Research Output by Country
- Substance Use Disorders Prevalence
- Demographic Disparities
- Ethnic and Racial Considerations
- National Statistics
- Key Indicators
- Trends Over Time
- Research Contributions
- Impact of Addiction
- Family Dynamics
- Role of Enablers
- Children of Addicted Parents
- Health Disparities and Social Determinants
- Treatment and Recovery
- Recovery Dynamics
- Factors Supporting Recovery
- Community Engagement and Resilience
- Policy and Prevention
- Strategic Areas for Action
- Legislative Measures and Standards
- Addressing Barriers to Care
- Community Engagement
- Challenges and Barriers
- Geographical and Insurance Disparities
- Social Determinants of Health
- Cultural Sensitivity and Language Barriers
- Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
- The Need for Comprehensive Approaches
- Recent Initiatives and Studies
- Global Advocacy and Strategic Actions
- Research Landscape and Policy Implications
- Community-Level Interventions
- Addressing Health Disparities
- Innovative Treatment Gaps
- Substance Abuse Trends 2024
- Prescription Drug Misuse Statistics
- Impact of Addiction on Marginalized Communities
- Teen Drug Use and School Students
- Veterans and Substance Abuse
- Addiction in the Workforce
- Gender Disparities in Addiction Rates
- Criminal Drug Laws and Addiction
- Addiction and Mental Health Correlation
- Recreational Marijuana and Legal Implications
- Addiction Treatment Success Rates and Challenges
- Addiction and Technological Interventions
- Addiction and Overdose Deaths
- Prescription Opioids and Risk of Addiction
- Substance Misuse in Youth
- Addiction and Socioeconomic Status
- Alcohol Addiction and Public Health
- Cocaine Use and Related Disorders
- Prescription Stimulants and Academic Pressure
- Addiction and Legal Implications
- Addiction and Family Dynamics
- Addiction in Marginalized Populations
- Nonfatal Drug Overdoses and Healthcare Interventions
- Addiction and Co-Occurring Disorders
- Addiction and Telemedicine Services
- Addiction and Public Awareness Campaigns
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- How Does the Burden of Substance Use Impact Society in 2024?
- What Are the Current Statistics on Overdose Deaths in the U.S. for 2024?
- How Does the Use of Illicit Drugs Affect Mental Health in 2024?
- What Are the Primary Risk Factors for Opioid Addiction in 2024?
- What Is the Status of Teen Drug Use in 2024?
- What Are the Main Challenges Faced by the Biden-Harris Administration in Combating the Opioid Epidemic?
- How Has the Opioid Epidemic Affected Military Veterans in 2024?
- What Are the Key Trends in Substance Use Disorder Treatment Success Rates in 2024?
- How Does Addiction Impact Employment Opportunities in 2024?
- What Are the Implications of Prescription Drug Abuse for the Healthcare System in 2024?
- What Are the Rates of Substance Abuse Among College Students in 2024?
- How Do Drug Overdoses Affect Marginalized Communities in 2024?
- What Role Do Prescription Stimulants Play in the Current Addiction Crisis?
- How Does Marijuana Use Disorder Affect Individuals in 2024?
- What Are the Statistics on Nonfatal Drug Overdoses in 2024?
- How Are Addiction Treatment Costs Affecting Accessibility in 2024?
- What Is the Relationship Between Mental Health and Addiction in 2024?
- How Does Alcohol Abuse Contribute to the Addiction Crisis in 2024?
- What Are the Trends in Behavioral Addiction Statistics in 2024?
- How Does Addiction Affect Family Dynamics in 2024?
- What Are the Implications of the 2024 Addiction Crisis for Public Health Policy?
- References
The 2024 Addiction Statistics reveal a critical public health crisis in the United States, highlighting the widespread prevalence and complex nature of addiction affecting millions. In 2022, nearly 50 million Americans aged 12 and older experienced substance use disorders (SUDs), encompassing both alcohol and drug-related issues.[1][2]
With a staggering 48.7 million individuals impacted, the statistics underscore the urgency for effective intervention strategies and increased awareness of addiction as a chronic condition that transcends socioeconomic and demographic boundaries. Addiction manifests in various forms, including substance use disorders, behavioral addictions, and co-occurring mental health issues, complicating treatment efforts and recovery outcomes.
The 2024 data indicates significant disparities across demographics, with notable variations in prevalence rates among different racial and ethnic groups.[3][4] Moreover, socioeconomic factors contribute to the challenges faced by those seeking treatment, exacerbating existing health disparities and limiting access to care.[5][6] The need for comprehensive and culturally responsive treatment approaches is paramount to addressing these multifaceted issues effectively.
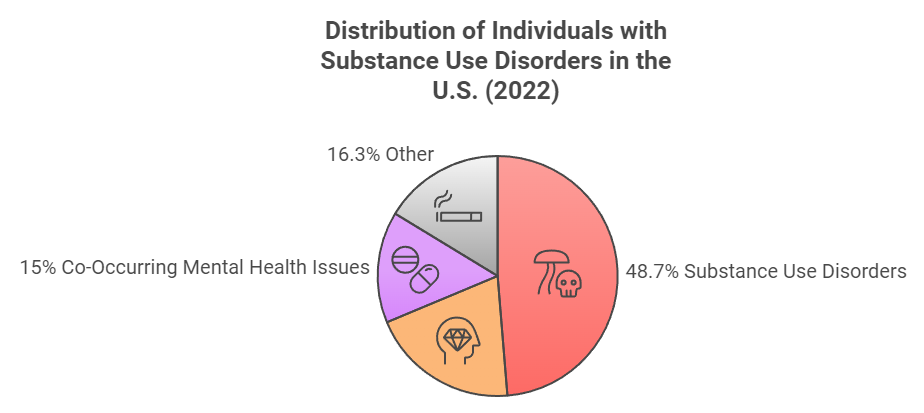

Controversies surrounding addiction statistics often revolve around the stigma attached to substance use and the barriers individuals face in accessing care. A significant proportion of those with SUDs are not receiving adequate treatment, with only 9.1% of individuals with co-occurring mental health disorders obtaining necessary support.[2][7]
Furthermore, the impact of family dynamics and enabling behaviors adds complexity to the recovery process, indicating that addiction is not just an individual issue but a societal one that requires collective action and understanding.[8][9]
As the nation grapples with these sobering statistics, the 2024 Addiction Statistics report serves as a crucial tool for informing policy, guiding research, and fostering public discourse on the need for integrated care solutions to combat this pervasive crisis. Recognizing addiction as a significant health issue is essential for advancing treatment efforts, supporting affected families, and ultimately fostering a more equitable approach to healthcare for all individuals struggling with addiction.[10][11]

Types of Addiction
Addiction can manifest in various forms, each with unique characteristics and challenges. The most commonly recognized types include substance use disorders, behavioral addictions, and co-occurring mental health issues.
Substance Use Disorders
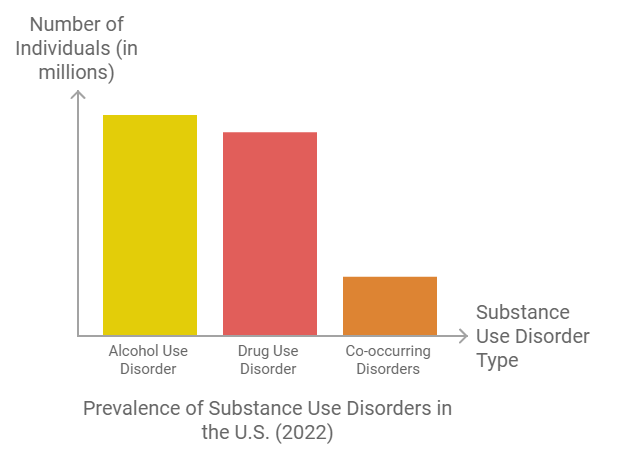
Substance use disorders (SUDs) are chronic, treatable conditions that affect millions of individuals. In 2022, approximately 48.7 million Americans aged 12 or older experienced a SUD, with alcohol use disorder (AUD) being the most prevalent, affecting around 29.5 million people. Additionally, 27.2 million individuals had a drug use disorder, with a notable overlap as 8.0 million of those with a drug use disorder also had an alcohol use disorder[1][2].
SUDs are characterized by continued substance use despite negative consequences, and they often involve cycles of relapse and recovery[1].

Behavioral Addictions
Beyond substance use, behavioral addictions, such as gambling addiction and sex addiction, follow similar patterns of dysfunction. Like substance use disorders, these addictions often become primary coping mechanisms for underlying issues, leading individuals to neglect responsibilities and relationships[3]. The dynamics of behavioral addictions are comparable to those seen in substance use, highlighting the pervasive nature of addictive behaviors.

Co-Occurring Disorders
Addiction frequently coexists with other mental health disorders, complicating treatment approaches. Individuals with SUDs may also suffer from conditions like anxiety, depression, or bipolar disorder, which can exacerbate their addictive behaviors[4]. The interaction between mental health issues and addiction necessitates a comprehensive treatment strategy that addresses both realms to improve recovery outcomes.

Enabling Behaviors
Family dynamics can significantly influence the progression of addiction. For instance, enabling behaviors, where family members shield an addicted individual from the consequences of their actions, can perpetuate the cycle of addiction[5].
In these cases, family members might downplay the severity of the addiction or actively contribute to the individual’s substance use, further complicating recovery efforts.
Understanding the various types of addiction is essential for developing effective interventions and support systems that can address the complexities of this pervasive issue.
Global Statistics
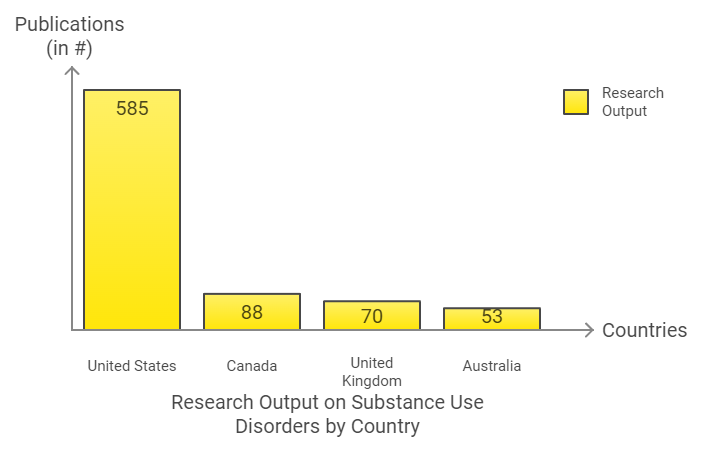
Research Output by Country
The issue of substance use disorders (SUDs) has garnered significant research interest globally, with a total of 935 publications documented. The United States leads in this research output, contributing 585 publications, which represents approximately 62.5% of the total. Following the U.S., Canada contributed 88 publications (9.4%), while the United Kingdom and Australia contributed 70 (7.5%) and 53 (5.7%) publications, respectively[6].

Substance Use Disorders Prevalence
Globally, the scale of substance use disorders is staggering. It is estimated that around 400 million people live with alcohol use disorders alone, highlighting a critical public health issue that transcends national borders[7]. In the United States, nearly 50 million individuals experienced a substance use disorder in the past year, with a concerning 9.1% of those with co-occurring mental health issues receiving treatment for both conditions[2].
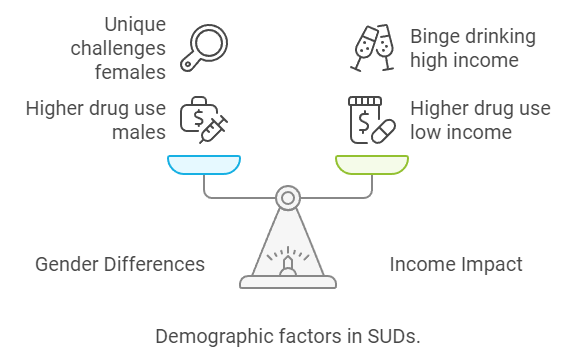
Demographic Disparities
The impact of SUDs varies significantly across different demographic groups. For instance, males generally exhibit higher rates of illicit drug use and alcohol dependence, although women are equally likely to develop SUDs and may face unique challenges such as cravings and relapse[2]. Additionally, socioeconomic status plays a crucial role; individuals with a median household income between $10,000 and $40,000 exhibit a higher prevalence of drug use and related emergency room visits, while binge drinking is more common among those with higher incomes[8].

Ethnic and Racial Considerations
Healthcare disparities further complicate the landscape of addiction. A significant proportion of racial and ethnic minority populations are affected by SUDs, yet they often face barriers to accessing treatment. This issue is compounded by the increasing diversity of the U.S. population, with 42.2% identifying as belonging to a racial or ethnic minority group[9]. Addressing these disparities is essential for improving healthcare outcomes and ensuring equitable treatment for all individuals affected by addiction[10].

National Statistics
The National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) provides key national indicators related to substance use, mental health issues, and treatment among the civilian, noninstitutionalized U.S. population aged 12 or older. The latest reports, covering data from 2021 to 2023, highlight trends and disparities in substance use and mental health across various demographics, including age and race/ethnicity.[11][12].
Key Indicators
Recent NSDUH data outlines significant metrics such as rates of tobacco, alcohol, and illicit drug use, along with the prevalence of substance use disorders (SUDs), major depressive episodes (MDEs), and co-occurring mental health disorders.[11][12][13]. Notably, the reports emphasize the complexity of dual diagnoses, where individuals experience both mental health and substance use disorders simultaneously. This underscores the necessity for integrated treatment approaches to address the intertwined nature of these issues.[6][12].

Trends Over Time
Analysis of NSDUH findings reveals patterns in substance use and mental health that have evolved over the years. For instance, there has been a significant increase in the initiation of substance use among youth, alongside rising rates of substance use disorders and mental health challenges among various age groups.
The data indicates a marked increase in the number of individuals seeking treatment for these issues, reflecting both growing awareness and the urgent need for effective intervention strategies.[11][12].
Research Contributions
The landscape of research surrounding substance use and mental health has grown significantly, with a total of 935 research articles published since the mid-1990s. The United States has been the largest contributor, producing approximately 62.5% of these publications.
Key areas of focus include the comorbidity of SUDs and mental health disorders, treatment interventions, and the epidemiological implications of these conditions, all of which are critical in shaping future healthcare policies and clinical practices.[6][12].
Impact of Addiction
Family Dynamics
Addiction is often referred to as a chronic “family disease,” indicating its pervasive effects on the entire family unit. As noted, every member of an addicted family is impacted by the addiction, adopting various coping strategies to manage the stress associated with living with an addict. Unfortunately, many of these coping mechanisms can have long-lasting negative effects, persisting even after the addict achieves sobriety, passes away, or exits the family environment[3][14].
The chaos of addiction creates an unpredictable home life, particularly for children, who may experience emotional neglect and abuse, leading to feelings of embarrassment, shame, and anger[3].

Role of Enablers
Family members often unintentionally enable addiction through their actions. For instance, they may protect addicted individuals from the consequences of their behavior or downplay the severity of the situation to avoid confrontation. In some cases, family members might actively sabotage recovery efforts, especially if they share similar addiction issues, thereby perpetuating the cycle of dysfunction[14][5]. This dynamic can create an environment that nurtures addiction rather than supporting recovery.
Children of Addicted Parents
The prevalence of substance use disorder (SUD) among parents significantly impacts their children. Statistics show that approximately 20.4 million people in the United States were diagnosed with SUD in the past year, highlighting the ripple effects of addiction on families[15]. Children raised in households with addicted parents often bear the emotional burden of chaos, leading to various behavioral and emotional challenges as they grow older[3].
Dr. Murray Bowen’s family systems theory underscores that each family member influences one another, which is disrupted by the presence of addiction, creating a complex web of interrelated issues that must be addressed for healing to occur[14].

Health Disparities and Social Determinants
Addiction does not discriminate, affecting individuals across different social and economic backgrounds. However, social determinants of health, such as poverty and stigma, can exacerbate the challenges faced by those struggling with addiction[15]. These factors contribute to significant health disparities, limiting access to effective treatment and support services.
The complexities of addiction are compounded by co-occurring mental health disorders, further complicating the landscape for treatment and recovery[16]. Understanding these social determinants is essential for creating equitable health solutions that can address both addiction and its associated outcomes effectively[17].
Treatment and Recovery
Treatment and recovery from substance use and mental health disorders are critical components in addressing the ongoing addiction crisis in the United States. According to a recent report by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), recovery is characterized by continual growth and improvement in one’s health and wellness while managing setbacks, which are a natural part of life.[18]
The report emphasizes a whole-health approach, demonstrating that recovery is achievable for those affected by these conditions when supported by comprehensive, individualized care.[18]
Recovery Dynamics
Research indicates that recovery is often a long-term process, typically taking about eight years or longer to achieve sustained remission, even with high-quality treatment and care.[19] A significant gap persists between the number of individuals needing treatment and those actually receiving it, attributed to barriers such as access and affordability.[19]
Moreover, relapse rates for substance use disorders are high, estimated to be between 40% and 60%, which underscores the chronic nature of addiction and the necessity for ongoing support and treatment adjustments.[19]
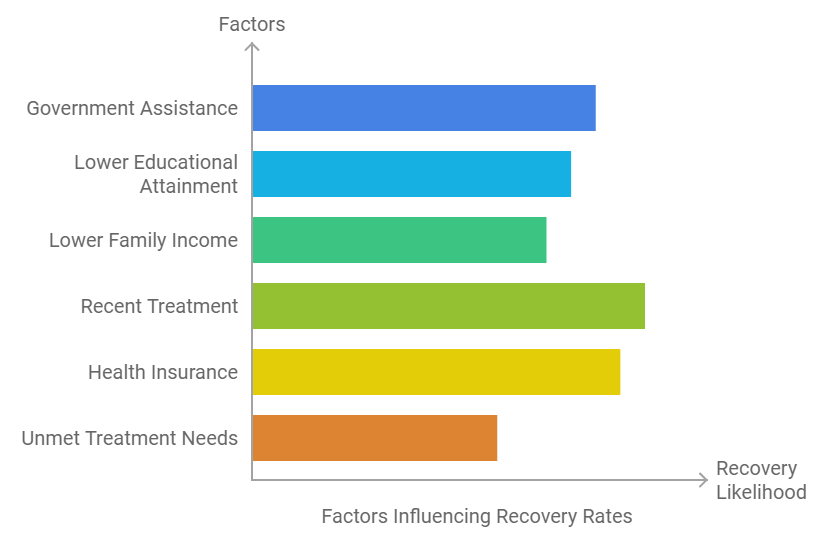
Factors Supporting Recovery
Key findings from SAMHSA’s report reveal that certain factors can enhance the likelihood of recovery from substance use and mental health disorders. Adults who participated in government assistance programs, had lower educational attainment, or lower family income were generally more likely to be in substance use recovery, although less so for mental health recovery.[18]
Additionally, mental health recovery was notably more prevalent among those who received treatment in the past year and those with health insurance.[18][20] The need for effective treatment is further highlighted by the observation that adults who felt they needed mental health treatment but did not receive it had lower recovery rates.[18]

Community Engagement and Resilience
During the COVID-19 pandemic, many individuals in recovery exhibited resilience, reporting minimal impacts on their behavioral health.[18] Access to harm reduction services, such as naloxone and fentanyl test strips, has also been recognized as a source of hope and community support during challenging times.[20]
The Biden-Harris Administration has made significant investments in improving access to mental health care and substance use treatment, totaling over $4.4 billion through various programs.[18]

Policy and Prevention
The growing public health crisis of substance use disorders (SUDs) necessitates urgent and comprehensive policy responses. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), substance use significantly harms individual health, leading to chronic diseases and mental health conditions, and results in millions of preventable deaths annually.[7]
To address these challenges, the WHO emphasizes the importance of achieving Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) target 3.5 by 2030, which aims to reduce alcohol and drug consumption and improve access to effective treatment for SUDs.[7]
Strategic Areas for Action
To mitigate the health and social burden of substance use, various strategic actions are recommended.[7]
Legislative Measures and Standards
In the United States, recommendations have been made for Congress to legislate national model standards for state licensure of addiction treatment programs. This would involve adhering to the most current edition of The ASAM Criteria, which defines levels of care for addiction treatment.[21]
Additionally, the federal government is urged to provide resources necessary for the development of performance measures in addiction treatment, ensuring they are patient-centered and focused on recovery as an ongoing process.[21]
Addressing Barriers to Care
Efforts must also be made to eliminate barriers to access and delivery of mental health and substance use services. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the need for policies that enhance telehealth coverage and ensure parity in insurance coverage for mental health and substance use services.[22]
Furthermore, adapting structural programs to reduce disparities in social determinants of health, particularly among racial and ethnic minority groups, is vital for comprehensive care.[22]
Community Engagement
At the community level, building partnerships with local organizations is crucial for increasing trust and decreasing stigma surrounding SUD treatment. Culturally responsive treatments can be developed through community engagement, with trusted local entities serving as conduits for information and resources.[9]
This collaboration is essential for establishing and maintaining support for recovery from addiction and ensuring that treatment approaches are tailored to meet the unique needs of diverse populations.[9]


Challenges and Barriers
Accessing treatment for substance use disorders (SUDs) is fraught with numerous challenges that impede timely and effective care. Common barriers include limited access to healthcare facilities, transportation difficulties, lack of insurance coverage, and the cultural stigma surrounding addiction treatment.[23][15].
Geographical and Insurance Disparities
Geographical disparities significantly hinder access, particularly in rural areas where resources are scarce. These limitations are exacerbated by insurance disparities, which restrict coverage for mental health services and impose stringent criteria for reimbursement.[6][22] As a result, individuals with dual diagnoses often experience poorer health outcomes due to the compounded complexity of their conditions.[6][24]
Social Determinants of Health
Social determinants of health, including poverty, homelessness, and social stigma, contribute to the severity of addiction and hinder recovery efforts. The stigma associated with substance use can create additional barriers to seeking help, as individuals may feel shame or fear judgment from healthcare providers and the broader community.[15][25]
This stigma not only discourages people from pursuing treatment but also perpetuates a cycle of silence around addiction issues.
Cultural Sensitivity and Language Barriers
Language barriers and cultural insensitivity in healthcare settings can alienate marginalized individuals who are seeking SUD services. Cultural perceptions of addiction can influence how it is acknowledged and addressed, making culturally competent care essential for effective treatment.[23][15]
In fact, Black patients were found to be half as likely to receive treatment following a non-fatal overdose compared to their Hispanic and White counterparts, highlighting the disparities that exist within different communities.[23]
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic further disrupted access to mental health and substance use services, necessitating adaptations in service delivery, including telehealth options.[22] Structural programs have been proposed to reduce preexisting disparities, aiming to address social determinants of health and ensure that vulnerable populations receive appropriate care during such crises.[22]
The Need for Comprehensive Approaches
Efforts to mitigate these challenges must focus on enhancing treatment capacity, scaling up training for healthcare professionals, and improving multi-level monitoring systems to better address the needs of individuals with SUDs and co-occurring disorders.[7]
Addressing these barriers holistically is essential for improving health outcomes and ensuring equitable access to care for all individuals affected by addiction.
Recent Initiatives and Studies
Global Advocacy and Strategic Actions
Efforts to address substance use disorders (SUDs) have seen a renewed focus on strategic areas aimed at reducing health and social burdens. Governments and partners are encouraged to intensify actions in eight key areas, which include increasing awareness through coordinated global advocacy campaigns and strengthening prevention and treatment capacities within health and social care systems[7].
A significant component of this initiative is the re-commitment to the Global Alcohol Action Plan 2022-2030, particularly focusing on the SAFER package[7].


Research Landscape and Policy Implications
Recent studies highlight the growing research interest in dual diagnosis—comorbid substance use and mental health disorders—since the late 1980s. This research has unveiled crucial insights into treatment and intervention needs, indicating a necessity for evidence-based integrated approaches that concurrently address both disorders[6].
A landscape analysis has identified emerging topics in dual diagnosis research, such as neurobiological factors and the impact of sociocultural influences, which reflect a shift towards a more holistic understanding of these conditions[6][23].
Community-Level Interventions
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) launched the HEALing Communities Study in 2020, aiming to engage addiction-affected communities in the research process. This project, operating in 67 communities impacted by the opioid crisis, strives to reduce opioid-linked overdose deaths by 40% over three years. It emphasizes the importance of social factors and community characteristics in crafting effective interventions[26].
Furthermore, findings suggest that policies should prioritize increasing service capacity for mental health and substance use disorder treatment in vulnerable communities, with potential funding sources identified for targeted interventions[27][28].
Addressing Health Disparities
Efforts to combat SUDs in marginalized populations necessitate a comprehensive approach that recognizes the underlying social determinants of health. Providing culturally sensitive, trauma-informed care while reducing stigma is vital for effective community-based interventions[23][29]. Tailored strategies for these populations can significantly contribute to reducing systemic health disparities and fostering a more equitable society[23].
Innovative Treatment Gaps
Amidst the rising stimulant drug use and a more contaminated drug supply, recent research has uncovered significant gaps in access to treatment and harm reduction services. Targeted interventions are urgently required to address these challenges effectively and to mitigate the ongoing overdose crisis[29][24].
The flexibility of these strategies allows them to complement existing treatment plans, thereby enhancing overall recovery approaches for individuals facing dual diagnosis or other substance-related issues[24].
Substance Abuse Trends 2024
Substance abuse trends in 2024 continue to reveal alarming patterns involving illicit drugs and prescription drugs. With the increasing prevalence of opioid use disorder, prescription opioids remain a significant factor in both overdose deaths and the burden of substance use in the U.S.
The Mental Health Services Administration continues to emphasize the need for broader access to mental health services to mitigate these issues. Addressing the impact of prescription drug abuse and opioid overdoses remains crucial for reducing the overall rate of drug overdoses.
Prescription Drug Misuse Statistics
Prescription drug misuse statistics show a rise in the abuse of prescription pain pills, prescription pain killers, and prescription stimulants among various demographics, especially among people ages 18 to 34. The National Survey on Drug Use and Health has indicated a significant increase in misuse, suggesting a growing concern over the potential for abuse of these substances.
Prescription drug abuse often serves as a gateway to harder drug use, further complicating treatment efforts and increasing addiction to drugs overall.


Impact of Addiction on Marginalized Communities
Addiction in marginalized communities, such as Native Americans and African Americans, is particularly concerning due to disparities in access to proper care. According to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health Detailed Tables, African Americans and Native Americans experience disproportionately higher rates of substance abuse disorder.
Additionally, socioeconomic challenges, combined with barriers like lack of health insurance, amplify the impact of illicit drug supply and substance abuse within these groups. Addressing these disparities through culturally sensitive approaches is imperative for promoting equitable access to addiction treatment.
Teen Drug Use and School Students
Teen drug use remains a significant issue, with the National Institute on Drug Abuse highlighting increases in marijuana use disorder and other addictive substances among 12th graders and 10th graders. School students who experiment with popular drugs face an increased risk of addiction, which can result in serious physical health issues, including heart conditions and complications involving the nervous system.
Adolescence is a critical period for intervention, making the role of school-based interventions and mental health counselor support crucial. Education on the risks of addictive substances is necessary for reducing experimentation among school students.
Veterans and Substance Abuse
Military veterans, particularly those served by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, continue to struggle with substance use disorders. Female veterans and homeless veterans are among the groups at highest risk, frequently facing challenges such as opioid addiction and prescription drug abuse.
The Department of Veterans Affairs has focused on promoting access to health care providers who can offer specialized services for veterans with chronic pain, a common reason for opioid use disorder. Addressing mental health crises among veterans through both inpatient treatment and outpatient treatment is key for improving recovery outcomes.
Addiction in the Workforce
The impact of addiction on employment is another critical aspect of the hidden addiction crisis. Addiction to psychoactive substances, including psychostimulants with abuse potential, can severely impair workplace performance and increase absenteeism.
Workplace programs focusing on addiction treatment and prevention are becoming increasingly important to support employees facing the risk of addiction. Proper care by health care providers, combined with addiction prevention strategies, can improve productivity and reduce substance misuse statistics in the workforce.
Gender Disparities in Addiction Rates
Addiction rates among men and women show notable differences in terms of substance abuse and co-occurring disorders. Women, for instance, often face unique risk factors such as intimate partner violence, which contributes to higher rates of mood disorders and alcohol addiction.
According to the National Survey on Drug Use, women are more likely to struggle with prescription drug misuse, particularly prescription stimulants, while men tend to have higher rates of illegal drug use. Addressing these gender disparities is vital for tailoring effective addiction intervention success strategies.
Criminal Drug Laws and Addiction
Criminal drug laws play a significant role in shaping how addiction is addressed within society. Strict enforcement of laws against illegal drug users often leads to punitive rather than rehabilitative outcomes, exacerbating the hidden addiction crisis.
Efforts to reform drug policy are being discussed to focus more on rehabilitation and harm reduction rather than criminalization. Implementing addiction harm reduction strategies and supporting addiction recovery community integration can improve the long-term outcomes for those with a substance abuse disorder.
Addiction and Mental Health Correlation
There is a strong correlation between addiction and mental health, with many individuals facing dual diagnosis statistics that highlight the complexity of treating both mental illness and substance use disorder. Data from the National Institute on Drug Abuse indicates that people with substance use frequently experience co-occurring mental illnesses, complicating the recovery process.
Integrated care approaches that address both substance use and mental health concerns are critical for improving addiction treatment outcomes. Access to mental health services is essential for individuals struggling with both addiction and mental health issues.
Recreational Marijuana and Legal Implications
The legalization of recreational marijuana in some states has also influenced substance abuse trends 2024, contributing to both an increase in marijuana use disorder and discussions around addiction and public health policies. Marijuana, although plant-based, is still categorized as a psychoactive drug, and its increased accessibility raises concerns regarding the potential for abuse.
The rate of overdose death linked to illicit substance use remains a significant challenge that requires a balance between legalization policies and effective public health strategies. Implementing guidelines for responsible recreational marijuana use is critical to avoid unintended addiction outcomes.
Addiction Treatment Success Rates and Challenges
The success rates of addiction treatment vary widely, influenced by factors such as addiction severity, co-occurring disorders, and access to proper care. Addiction treatment patient satisfaction is highest among those receiving individualized care through programs like those offered by American Addiction Centers.
Outpatient success rates tend to be lower compared to inpatient outcomes, particularly for individuals with alcohol-related death risks or opioid addiction. Expanding access to admissions navigators and addiction treatment affordability initiatives can help improve addiction treatment completion rates.
Addiction and Technological Interventions
Innovative approaches like addiction treatment telehealth options and digital health tools are becoming more prominent in addressing addiction, particularly for those in rural or underserved areas. Telemedicine effectiveness has shown promise for addiction treatment, especially for people with substance use who face challenges accessing traditional healthcare settings.
Virtual therapy outcomes and addiction recovery mobile applications provide essential support, especially for individuals managing addiction withdrawal symptoms. These technological interventions are reshaping how addiction treatment and recovery are approached in the digital age.
Addiction and Overdose Deaths
Drug overdose deaths continue to be a major issue, particularly among people with substance use who have a history of opioid use disorder. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported rising overdose deaths attributed to dangerous drugs like fentanyl and synthetic drugs.
Prevention efforts, such as access to naloxone, are vital for reducing the risk of overdose death and improving community outcomes. Increased education on overdose risks is also essential to reduce fatalities.
Prescription Opioids and Risk of Addiction
Prescription opioids have a high potential for abuse, especially among individuals dealing with chronic pain. Improper use of prescription pain relievers has led to widespread prescription drug abuse.
The burden of substance use, including prescription opioid addiction, requires careful management by health care providers to minimize the risk of addiction while ensuring effective pain management. Appropriate use of prescription pain killers is crucial in preventing opioid addiction.
Substance Misuse in Youth
Youth substance use statistics indicate concerning trends, with increased experimentation among 8th graders and 10th graders involving illicit drugs and prescription drugs. The National Survey of Drug Use and Health Releases reveals rising rates of substance misuse in school students, underscoring the need for preventive measures and early interventions to reduce the rates of substance abuse among teens.
Targeted education on the dangers of popular drugs is crucial to mitigate youth involvement in substance use. The role of parents and schools in preventing youth substance misuse cannot be overstated.
Addiction and Socioeconomic Status
Addiction and socioeconomic status are closely linked, with individuals from poorer countries and lower income levels being more susceptible to substance abuse disorders. Income disparities significantly affect access to addiction treatment and support services, creating a cycle of addiction that is difficult to break.
In contrast, those in richer countries often have better access to addiction treatment, although addiction remains prevalent across all income levels. Addressing income-related barriers is essential for promoting equitable addiction treatment access.
Alcohol Addiction and Public Health
Alcohol addiction remains a pervasive issue, contributing to a high rate of alcohol-related deaths each year. Public health strategies focused on reducing alcohol abuse prevalence include increasing awareness and expanding access to treatment for individuals with alcohol abuse issues.
Alcohol abuse also exacerbates the burden of substance use, affecting not only physical health but also contributing to mental health crises. Preventive measures are essential to lower the rates of alcohol addiction and its related health complications.
Cocaine Use and Related Disorders
Cocaine use disorder continues to be a serious problem, contributing to numerous physical health issues, including heart disease and panic disorders. Cocaine overdoses have increased, with the CDC highlighting the role of both powdered and crack cocaine as contributing factors.
Addressing the rate of cocaine use requires a combination of treatment, prevention, and harm reduction strategies to mitigate the risks associated with this class of drug. Community-level interventions are vital to prevent cocaine-related complications.
Prescription Stimulants and Academic Pressure
The misuse of prescription stimulants, often used as nervous system stimulants, is prevalent among college students facing academic pressure. Prescription stimulants like Adderall and Ritalin are often abused to enhance concentration, but this misuse can lead to addiction and other health issues.
School-based interventions and education on the risks of prescription stimulant misuse are crucial in reducing addiction among students. Highlighting the potential risks of prescription drug abuse can prevent academic pressure from leading to harmful substance use.
Addiction and Legal Implications
Addiction carries significant legal implications, particularly for individuals caught using or distributing illegal drugs. Criminal drug laws vary by region, but punitive measures often fail to address the root causes of addiction.
Drug policy reform aimed at rehabilitation rather than incarceration is being pursued as a means to reduce the societal impact of addiction and promote more effective recovery pathways. Supportive legal frameworks can help in reducing repeat offenses and encouraging treatment.
Addiction and Family Dynamics
The impact of addiction on families can be profound, affecting all members of a household. Addiction often leads to strained relationships, financial difficulties, and emotional stress.
Family therapy and support groups are essential components of addiction treatment, helping families to heal and support their loved ones through the recovery process. Addressing the needs of family members can be instrumental in the success of addiction recovery.
Addiction in Marginalized Populations
Marginalized populations, including American Indian and Latino Americans, are disproportionately affected by addiction and face additional barriers to accessing treatment. The Bureau of Indian Affairs and other organizations work towards providing targeted support to these communities.
Addressing addiction in these populations requires culturally sensitive interventions and increased funding for community resources. Ensuring equitable access to care can help alleviate the impact of addiction in marginalized groups.
Nonfatal Drug Overdoses and Healthcare Interventions
Nonfatal drug overdoses are a growing concern, leading to increased hospital admissions and healthcare costs. Prompt intervention by health care providers can prevent nonfatal drug poisonings from escalating into fatal events.
Expanding access to addiction and emergency care services is essential to reduce the rates of nonfatal overdoses and improve recovery outcomes. Training health professionals to respond quickly can save lives and improve patient outcomes.
Addiction and Co-Occurring Disorders
Addiction often co-occurs with other mental health disorders, such as mood disorders and anxiety. The prevalence of co-occurring disorders complicates treatment and requires integrated care approaches.
Addressing both addiction and mental health concurrently can improve long-term recovery outcomes and reduce relapse rates among those with a substance abuse disorder. Coordinated care strategies are necessary for patients with dual diagnoses.
Addiction and Telemedicine Services
Telemedicine services are becoming an important tool in addiction treatment, particularly for those in remote or underserved areas. Addiction treatment telemedicine effectiveness has been demonstrated through improved access to care and treatment adherence rates.
Virtual counseling and remote support groups help individuals maintain their recovery journeys without the need for in-person visits. The flexibility of telemedicine helps overcome geographical barriers to addiction treatment.
Addiction and Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns are instrumental in reducing addiction stigma and promoting prevention. The Biden-Harris Administration has made significant investments in addiction awareness programs, focusing on education, prevention, and the importance of seeking treatment.
Increasing public understanding of addiction as a health issue rather than a moral failing can foster greater support for individuals struggling with substance use. Effective campaigns are key to creating a more supportive and informed society.
Conclusion
The 2024 Addiction Statistics paint a complex picture of the ongoing substance use crisis in the United States and globally. While progress has been made in understanding the multifaceted nature of addiction and developing more comprehensive treatment approaches, significant challenges remain. The data underscores the need for continued efforts in research, policy development, and community engagement to address the root causes of addiction and improve access to effective care.
Moving forward, it is crucial to:
- Implement evidence-based policies that prioritize prevention and early intervention.
- Address social determinants of health and reduce disparities in access to treatment.
- Enhance cultural competency in addiction treatment services.
- Invest in innovative treatment approaches and harm reduction strategies.
- Foster community partnerships to reduce stigma and support long-term recovery.
By taking a holistic and compassionate approach to addiction, we can work towards a future where fewer individuals and families are impacted by this pervasive health crisis. The journey to recovery is challenging, but with continued dedication to understanding and addressing addiction, there is hope for meaningful progress in the years to come.
From Embrace Inner Chaos to your inbox
Transform your Chaos into authentic personal growth – sign up for our free weekly newsletter! Stay informed on the latest research advancements covering:
Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD)
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does the Burden of Substance Use Impact Society in 2024?
The burden of substance use in 2024 is seen in the significant strain it places on healthcare systems, social services, and the economy. Substance abuse leads to increased hospital admissions, the overuse of emergency services, and a growing number of overdose deaths.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that these medical costs are only a fraction of the broader financial toll that includes lost productivity, criminal justice involvement, and long-term health issues. The cumulative effects of substance use exacerbate poverty, strain community resources, and worsen quality of life for affected families.
Aside from the healthcare costs, substance use also leads to extensive social consequences. Families often face emotional strain, financial instability, and the stigmatization of having a loved one with a substance use disorder.
Community-based services, such as housing and child protective services, are also deeply affected by the rise in cases of drug dependency and its impact on family structures. Furthermore, it puts an added burden on law enforcement due to the direct link between addiction and crime rates, often involving illegal drug activities and theft.
What Are the Current Statistics on Overdose Deaths in the U.S. for 2024?
As of 2024, overdose deaths in the U.S. have continued to increase, fueled largely by synthetic opioids such as fentanyl. According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, overdose deaths involving opioids account for nearly 75% of all drug-related deaths.
The mortality rate is especially high among individuals with opioid use disorder, driven by the increasing availability of potent synthetic opioids, which are often mixed with other substances without the user’s knowledge. This unpredictability in drug composition significantly increases the risk of overdose.
Regional disparities also contribute to the rising death toll. States like West Virginia continue to have the highest rate of overdose deaths per capita, reflecting economic hardship and limited access to addiction treatment.
Social and economic factors, such as unemployment, lack of healthcare, and underfunded rehabilitation services, exacerbate these regional trends, making overdose deaths not only a medical issue but also a societal one.


How Does the Use of Illicit Drugs Affect Mental Health in 2024?
Illicit drug use in 2024 is closely linked with deteriorating mental health outcomes. Studies indicate that individuals who use drugs like methamphetamine, cocaine, and opioids are at an increased risk of developing anxiety, depression, and other severe mood disorders.
The National Survey on Drug Use and Health reveals that there has been a substantial rise in the co-occurrence of mental health disorders and substance abuse, often termed as a dual diagnosis. This condition makes treatment more complex, as both mental health and substance use must be managed simultaneously for effective recovery.
For many users, mental health conditions often precede substance use as they self-medicate to alleviate symptoms such as chronic anxiety, panic disorders, and depression. The use of drugs initially provides temporary relief, but over time, it exacerbates the underlying mental health conditions, creating a vicious cycle of dependency and worsening mental illness.
This dynamic is particularly evident among young people, with increasing rates of both mental health crises and illicit substance use reported in the age group of 18 to 25. The burden on the healthcare system is immense, with mental health services struggling to accommodate the rising number of individuals needing help.
What Are the Primary Risk Factors for Opioid Addiction in 2024?
In 2024, opioid addiction is primarily driven by a combination of genetic, environmental, and social factors. The American Addiction Centers emphasize that individuals with a family history of substance abuse are more likely to develop opioid addiction, as genetics play a significant role in determining susceptibility.
Other contributing factors include exposure to high-stress environments, such as military veterans experiencing PTSD, and individuals with chronic pain conditions who are prescribed opioids for pain management. Prescription opioids, initially given for legitimate medical purposes, often become a gateway to addiction.
Patients who use these drugs beyond their prescribed dose or duration are at a high risk of developing dependency. Improper prescribing practices, lack of education among healthcare providers regarding the addictive potential of these drugs, and inadequate patient follow-ups contribute significantly to the risk of addiction.
Additionally, individuals experiencing economic hardship or living in areas with limited access to healthcare are more vulnerable to opioid misuse. Social determinants such as unemployment, housing instability, and exposure to environments where drug use is prevalent also increase the likelihood of developing an opioid use disorder.
What Is the Status of Teen Drug Use in 2024?
Teen drug use in 2024 shows troubling trends, particularly with the rising consumption of prescription stimulants and marijuana among adolescents. According to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health Detailed Tables, the use of substances like marijuana and prescription stimulants has increased among 8th, 10th, and 12th graders.
These substances are often perceived as less dangerous compared to harder drugs, which has led to increased experimentation among teens. The ease of access to these drugs, sometimes through family prescriptions or social networks, has made them more common in schools.
Marijuana use among teenagers is particularly concerning, given its effects on developing brains. Studies indicate that marijuana use in adolescents can lead to long-term cognitive impairments, affecting memory, attention, and decision-making abilities.
This age group is also more vulnerable to developing marijuana use disorder, characterized by dependency and withdrawal symptoms, which is a significant public health concern. Marijuana is now widely accessible in states where recreational use is legal, contributing to the normalization of its use among young people.
What Are the Main Challenges Faced by the Biden-Harris Administration in Combating the Opioid Epidemic?
The Biden-Harris Administration faces numerous challenges in combating the opioid epidemic in 2024, including the escalating availability of fentanyl and the gaps in healthcare accessibility. One of the key issues is the illicit drug supply, which has been flooded with potent synthetic opioids, making it challenging for law enforcement agencies to control their distribution.
These substances are often mixed with other drugs like cocaine and heroin, significantly increasing the risk of overdose among users. Another challenge is ensuring equitable access to treatment across all communities, particularly in underserved areas.
Disparities in healthcare access have made it difficult for many people, especially in rural areas, to receive the necessary addiction treatment services. The administration is working to expand Medicaid and invest in community health initiatives to address these disparities, but the scale of the problem makes this a daunting task.
Moreover, the stigma surrounding opioid addiction prevents many individuals from seeking help, which exacerbates the issue. The administration is also grappling with the need for better prevention strategies, including tighter regulations on opioid prescriptions and increased education among healthcare providers regarding non-opioid alternatives for pain management.


How Has the Opioid Epidemic Affected Military Veterans in 2024?
In 2024, military veterans continue to face a high risk of opioid addiction, largely due to chronic pain resulting from their service. Many veterans suffer from severe physical injuries and PTSD, conditions often treated with prescription painkillers.
The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs has been actively working to reduce opioid prescriptions and increase access to alternative pain management options, including physical therapy and mental health services. However, the complexity of veterans’ healthcare needs has made this transition challenging.
Veterans with opioid use disorder often face barriers to receiving proper care, including stigma and inadequate resources. The rate of opioid overdose deaths among veterans has been rising, with many struggling to access comprehensive addiction treatment.
The availability of mental health and addiction services is still insufficient to meet the demand, especially in rural areas where many veterans reside, exacerbating their health issues. Addressing opioid addiction among veterans requires a multi-faceted approach, including increased funding for the Department of Veterans Affairs, better integration of physical and mental healthcare, and community-based support networks.
What Are the Key Trends in Substance Use Disorder Treatment Success Rates in 2024?
Substance use disorder treatment success rates in 2024 have shown some improvement, largely due to advancements in personalized treatment approaches and increased access to Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT). According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, treatment that combines medications like buprenorphine with counseling and behavioral therapies has been effective in helping individuals recover from opioid addiction.
MAT has been particularly successful in reducing relapse rates, especially among individuals struggling with severe opioid use disorder. However, the overall success of treatment varies widely depending on factors such as the availability of treatment resources, the severity of addiction, and the presence of co-occurring mental health conditions.
Rural areas still lag behind in providing adequate treatment options, which affects recovery outcomes. Success rates are highest when individuals have access to integrated services that address both substance use and mental health issues simultaneously.
Another key trend is the increased focus on long-term support through community-based programs and peer support groups. Recovery is a continuous process, and the risk of relapse remains high, especially during the first year after treatment.
How Does Addiction Impact Employment Opportunities in 2024?
In 2024, addiction continues to have a significant impact on employment opportunities, affecting individuals’ ability to secure and maintain jobs. Addiction can lead to job loss, decreased productivity, and increased absenteeism, which in turn affects one’s employability.
According to data from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, individuals with substance use disorders are more likely to face unemployment due to poor work performance and the challenges of balancing job responsibilities while struggling with addiction. Employers are often hesitant to hire individuals with a history of substance use due to concerns about reliability, workplace safety, and healthcare costs.
This stigma makes it difficult for those in recovery to reenter the workforce, even if they have successfully completed treatment. Additionally, addiction can lead to gaps in employment history, making it challenging for individuals to find stable, well-paying jobs.
Efforts to mitigate these challenges include initiatives such as workplace-based addiction treatment programs and incentives for employers to hire individuals in recovery. These programs aim to reduce the stigma associated with addiction, support recovery through stable employment, and ultimately lower relapse rates.
What Are the Implications of Prescription Drug Abuse for the Healthcare System in 2024?
Prescription drug abuse continues to place a considerable burden on the healthcare system in 2024. Abuse of prescription opioids, stimulants, and anti-anxiety medications leads to increased hospital visits, treatment costs, and emergency room overcrowding.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services notes that prescription drug misuse contributes to a significant portion of healthcare expenditure, as individuals abusing these drugs are more likely to require emergency care for overdoses and complications related to addiction. The misuse of prescription painkillers, in particular, often leads to opioid use disorder, further straining healthcare services.
Chronic misuse can result in long-term health complications such as liver damage, cardiovascular issues, and increased susceptibility to infections, necessitating ongoing medical care and support. The healthcare system’s ability to provide adequate treatment is often limited by a lack of specialized addiction care facilities and the high cost of treatment.
Additionally, healthcare providers face the challenge of managing patients’ pain without contributing to the risk of addiction. This dilemma underscores the need for better pain management strategies, including non-opioid treatments and patient education on the risks of prescription drug misuse.
What Are the Rates of Substance Abuse Among College Students in 2024?
In 2024, substance abuse rates among college students have remained high, driven by the pressures of academic performance, social dynamics, and the availability of substances. The National Survey on Drug Use and Health shows that alcohol and marijuana are the most commonly abused substances among college students.
These are followed by prescription stimulants like Adderall and Ritalin, which are often used to enhance academic focus. The use of these substances is often normalized in the college environment, contributing to higher rates of abuse.
The misuse of prescription stimulants among college students is particularly concerning, as it carries significant risks, including dependency, cardiovascular issues, and mental health problems. Many students use these drugs without a prescription, believing that they will improve their concentration and academic performance, despite the risks involved.
The social environment of college also plays a role, as the pressure to fit in and succeed academically can lead to increased substance use. Colleges and universities have attempted to address this issue through prevention programs, increased access to mental health services, and policies that limit the availability of substances on campus.
How Do Drug Overdoses Affect Marginalized Communities in 2024?
Drug overdoses have disproportionately affected marginalized communities in 2024, with racial and economic disparities contributing to higher overdose rates among these populations. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, African Americans, Native Americans, and Latino Americans face higher rates of overdose deaths compared to other groups.
These disparities are attributed to factors such as limited access to quality healthcare, higher rates of unemployment, and the presence of systemic biases within the healthcare system. Many marginalized communities also have limited access to addiction treatment services, which exacerbates the impact of drug overdoses.
Barriers such as a lack of health insurance, transportation difficulties, and the stigma associated with seeking help prevent many individuals from accessing life-saving interventions. The opioid epidemic has further deepened these disparities, as potent synthetic opioids like fentanyl have flooded illicit drug markets, putting users at an increased risk of overdose.
Efforts to reduce these disparities include targeted public health initiatives, increased funding for community health centers, and outreach programs aimed at increasing awareness and access to addiction treatment services. Addressing the overdose crisis in marginalized communities requires a multi-faceted approach that includes not only medical interventions but also social support systems and policies aimed at reducing inequality and improving healthcare access.
What Role Do Prescription Stimulants Play in the Current Addiction Crisis?
Prescription stimulants, such as Adderall and Ritalin, play a significant role in the addiction crisis in 2024, particularly among young adults and professionals seeking cognitive enhancement. The Drug Enforcement Administration reports that the misuse of these stimulants has increased, driven by the perception that they are safe compared to illicit drugs.
Many individuals use prescription stimulants to improve focus, boost energy, or cope with demanding work or academic schedules, often without understanding the risks involved. The misuse of prescription stimulants can lead to addiction, cardiovascular problems, and mental health issues such as anxiety and panic disorders.
These drugs have a high potential for abuse, especially when taken in larger doses or without a prescription. Users often develop a tolerance, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effects, which increases the risk of serious health complications, including overdose.
Efforts to curb the misuse of prescription stimulants include stricter prescribing regulations, educational campaigns on the risks of misuse, and increased availability of addiction treatment services for stimulant use disorder. Addressing this aspect of the addiction crisis requires both regulatory actions to limit access and preventive education to change perceptions about the safety of these drugs.
How Does Marijuana Use Disorder Affect Individuals in 2024?
Marijuana use disorder remains a significant public health issue in 2024, particularly as the use of marijuana becomes increasingly normalized with its legalization in many states. According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, marijuana use disorder affects approximately 10% of individuals who use the drug, with higher rates among those who begin using at a young age.
The disorder is characterized by dependence, withdrawal symptoms, and a negative impact on daily functioning, including work, school, and relationships. Individuals with marijuana use disorder often experience cognitive impairments, such as difficulties with memory, attention, and learning, which can persist even after stopping use.
The normalization of marijuana use, especially among teenagers and young adults, has led to an increase in the number of individuals developing dependence. This is concerning given the potential long-term effects of marijuana on the developing brain, which include impaired cognitive abilities and increased susceptibility to mental health issues.
Treatment for marijuana use disorder typically involves behavioral therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which focuses on identifying and changing problematic behaviors. Access to effective treatment is still limited, and there is a need for increased awareness and resources to address marijuana dependency, especially in light of its growing legal availability and social acceptance.
What Are the Statistics on Nonfatal Drug Overdoses in 2024?
Nonfatal drug overdoses in 2024 have been on the rise, indicating the widespread prevalence of substance use issues across the United States. According to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health Releases, nonfatal overdoses are more common than fatal overdoses, with many individuals experiencing repeated overdose incidents.
These nonfatal episodes often lead to long-term health complications, including respiratory issues, neurological damage, and increased vulnerability to future overdoses. The majority of nonfatal overdoses involve opioids, including prescription painkillers and synthetic opioids like fentanyl.
The rise in nonfatal overdoses is partly due to the increased availability of naloxone, an opioid overdose reversal drug, which has saved countless lives. However, while naloxone can prevent death, it does not address the underlying addiction, and many individuals continue to struggle with substance use following an overdose.
The healthcare system bears the cost of nonfatal overdoses, which often involve emergency room visits and extended hospital stays. To address the issue, there is a need for better post-overdose care that includes addiction treatment and follow-up services to prevent recurrent overdoses.
How Are Addiction Treatment Costs Affecting Accessibility in 2024?
In 2024, the high cost of addiction treatment continues to be a significant barrier to accessing care for many individuals struggling with substance use disorders. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration indicates that despite increased funding for public health initiatives, many individuals are unable to afford inpatient or outpatient treatment due to high out-of-pocket costs.
This is particularly true for those without insurance or with limited coverage, making comprehensive addiction treatment out of reach for many. Inpatient treatment, which provides 24-hour care and support, is often prohibitively expensive, and the lack of affordable alternatives forces many individuals to forego the level of care they need.
Outpatient services, while more affordable, may not provide the intensive support necessary for individuals with severe addiction, resulting in lower success rates for recovery. Additionally, the cost of medication-assisted treatment, which includes medications like methadone or buprenorphine, can also be a barrier for those in need.
To address these accessibility issues, there have been efforts to expand Medicaid and increase funding for addiction treatment programs, but significant gaps remain. The need for affordable, comprehensive treatment options is critical to ensuring that all individuals, regardless of income or insurance status, have the opportunity to recover from addiction.
What Is the Relationship Between Mental Health and Addiction in 2024?
In 2024, the relationship between mental health and addiction is well-recognized, with the co-occurrence of these conditions presenting a major challenge for healthcare providers. The National Alliance on Mental Illness reports that individuals with mental health disorders, such as depression or anxiety, are more likely to develop substance use disorders as they attempt to self-medicate their symptoms.
This phenomenon creates a dual diagnosis, where both mental health and addiction need to be treated simultaneously for effective recovery. The presence of a mental health disorder complicates addiction treatment, as untreated mental illness often leads to relapse and increases the difficulty of achieving long-term recovery.
Many individuals with dual diagnoses do not receive adequate care due to a lack of coordination between mental health and substance use services. This gap in treatment contributes to high rates of rehospitalization and poor outcomes for individuals struggling with both conditions.
Integrated treatment approaches that address both mental health and substance use simultaneously are shown to be the most effective. However, access to such care remains limited, with many treatment facilities specializing in either mental health or addiction but not both.
How Does Alcohol Abuse Contribute to the Addiction Crisis in 2024?
Alcohol abuse remains a significant component of the broader addiction crisis in 2024. The World Health Organization states that alcohol abuse contributes to a wide range of health problems, including liver disease, cardiovascular issues, and increased risk of injuries due to impaired judgment.
It is also associated with a higher likelihood of developing other substance use disorders, as individuals who abuse alcohol may be more prone to experimenting with drugs, thereby increasing their risk of addiction. The prevalence of alcohol abuse is particularly high among certain demographics, such as college students, where binge drinking is normalized, and among older adults who may turn to alcohol as a coping mechanism for loneliness or chronic pain.
Alcohol use is also linked to mental health issues, with many individuals using it to self-medicate anxiety or depression, which in turn exacerbates both their mental health and substance use problems. Efforts to curb alcohol abuse include public health campaigns aimed at reducing binge drinking, stricter regulations on alcohol sales, and increased access to treatment for alcohol use disorder.
Despite these efforts, alcohol remains one of the most widely abused substances, contributing significantly to the overall burden of addiction and highlighting the need for more comprehensive prevention and treatment strategies.
What Are the Trends in Behavioral Addiction Statistics in 2024?
Behavioral addictions, such as gambling, internet, and smartphone addiction, are increasingly recognized as significant public health issues in 2024. According to the American Psychiatric Association, behavioral addictions share many similarities with substance use disorders, including the compulsive nature of the behavior, withdrawal symptoms, and the negative impact on daily functioning.
The rise of technology and online platforms has led to an increase in the prevalence of behavioral addictions, particularly among younger populations. Internet and smartphone addiction have been linked to increased levels of anxiety, depression, and social isolation, as individuals become more reliant on digital interactions rather than face-to-face relationships.
These addictions can interfere with work, academic performance, and personal relationships, leading to significant negative consequences. The normalization of constant connectivity has made it difficult for individuals to recognize the harmful effects of excessive screen time.
Gambling addiction has also seen a rise, partly due to the increased availability of online gambling platforms. The ease of access and the immersive nature of online gambling make it highly addictive, with many individuals experiencing significant financial losses and deteriorating mental health as a result.
How Does Addiction Affect Family Dynamics in 2024?
Addiction continues to have a profound impact on family dynamics in 2024, creating an environment of stress, mistrust, and emotional instability. The National Council on Alcoholism and Drug Dependence reports that families with a member struggling with addiction often experience financial difficulties due to the costs associated with substance use, such as healthcare expenses, legal issues, and lost income.
These financial burdens can lead to tension and conflict, further straining family relationships. The emotional toll of addiction on families is significant, with many family members experiencing anxiety, depression, and a sense of helplessness.
The unpredictability of an addicted individual’s behavior can lead to a loss of trust and feelings of betrayal, especially when promises to quit are repeatedly broken. Children in these families are particularly vulnerable, often experiencing neglect, exposure to harmful behaviors, and a lack of stability, which can have long-term effects on their mental health and development.
Family support is crucial for successful recovery, yet the stigma surrounding addiction often prevents families from seeking help. Support groups and family therapy are effective in helping families cope with the challenges of addiction, fostering understanding, and rebuilding trust.
What Are the Implications of the 2024 Addiction Crisis for Public Health Policy?
The 2024 addiction crisis has significant implications for public health policy, necessitating a comprehensive approach that addresses prevention, treatment, and harm reduction. According to the American Public Health Association, the rise in substance use, overdose deaths, and the burden on healthcare systems highlights the need for policies that prioritize addiction as a critical public health issue.
Effective public health policy must include increased funding for addiction treatment, expansion of mental health services, and the implementation of harm reduction strategies, such as needle exchange programs and safe consumption sites. The addiction crisis also underscores the importance of integrating addiction treatment into primary healthcare.
Many individuals do not receive the help they need due to the separation of addiction treatment from general healthcare services. By incorporating addiction screening and treatment into primary care settings, healthcare providers can identify at-risk individuals earlier and provide timely interventions, thereby reducing the overall burden of addiction.
Public health policy must also address the social determinants of addiction, such as unemployment, lack of education, and housing instability, which contribute to higher rates of substance use. Policies aimed at improving economic stability, education, and access to healthcare can help reduce the prevalence of addiction and support long-term recovery.
References
[1] Fewer than half of U.S. jails provide life-saving medications for opioid use disorder
[2] Current Addiction Statistics: 2024 Data on Substance Abuse & Trends
[3] How Addiction Impacts the Family: 6 Family Roles in a Dysfunctional or Alcoholic Family
[4] Substance Use and Co-Occurring Mental Disorders | NIMH
[5] Dealing With Family Dynamics During Recovery
[6] Research landscape analysis on dual diagnosis of substance use and mental disorders
[7] Over 3 million annual deaths due to alcohol and drug use, majority are preventable
[8] Drug Use Statistics in the United States | September 2024 – Rehab.com
[9] Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities | Hazelden Betty Ford
[10] Annual Demographic Estimates: Canada, Provinces and Territories, 2024
[11] 2023 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) Releases – SAMHSA
[12] 2023 NSDUH Annual National Report | CBHSQ Data – SAMHSA
[13] Products – Data Briefs – Number 491 – March 2024 – Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
[14] Addiction and the Family Systems Model – NACoA
[15] Poverty, homelessness, and social stigma make addiction more deadly
[16] An integrative collaborative care model for people with mental illness and physical comorbidities
[17] National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)
[18] SAMHSA Releases New Data on Recovery from Substance Use and Mental Health Conditions
[19] Statistics on Drug Addiction Treatment and Recovery Rates in the US
[20] Fentanyl Statistics 2024: Latest Overdose & Addiction Data
[21] Government Strategies to Foster Ethical Addiction Treatment
[23] Substance Use Disorder Prevention and Treatment Services: A Social Work Perspective
[24] Promising Treatments for Dual Diagnosis | DualDiagnosis.org
[25] Social stigma creates barriers to treatment for people with substance use disorders
[26] NIH Aims to Expand Addiction Research Strategies Beyond the Brain – BrainFacts
[27] Social vulnerability linked with mental health and substance use disorders
[28] Social vulnerability linked with mental health and substance use disorders
[29] New Research Sheds Light on Treatment and Harm Reduction Gaps Among People Who Use Drugs



